miR-7 Reverses Breast Cancer Resistance To Chemotherapy By Targeting MRP1 And BCL2
- PMID: 31908478
- PMCID: PMC6924589
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S213780
miR-7 Reverses Breast Cancer Resistance To Chemotherapy By Targeting MRP1 And BCL2
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of non-coding RNAs that have been linked with breast cancer chemoresistance, which is a major clinical problem causing disease relapse and poor prognosis. miR-7 exerts several tumor suppressive activities.
Purpose: This study was designed to clarify whether and how miR-7 regulates breast cancer chemoresistance.
Methods: miR-7 level in breast cancer was determined by qRT-PCR analysis. Cell viability was assessed by MTS assay to quantify the IC50 value of paclitaxel and carboplatin. The targets of miR-7 were confirmed by luciferase reporter assay.
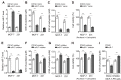
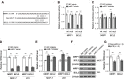
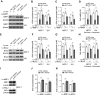
Results: Higher miR-7 expression predicts better pathological complete response (pCR) of breast cancer patients receiving paclitaxel/carboplatin chemotherapy. In vitro, miR-7 sensitizes breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) to paclitaxel and carboplatin, alone and in combination. In addition, we reveal that both the multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1) and anti-apoptotic B cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2) are targets of miR-7 in breast cancer cells. Furthermore, miR-7-induced sensitization of breast cancer to paclitaxel/carboplatin is markedly reversed by restoration of MRP1 and BCL2.
Conclusion: These findings show that miR-7 reverses breast cancer chemoresistance through suppressing MRP1 and BCL2, and also suggest that miR-7 may possess a predictive value and represent a therapeutic target in breast cancer chemotherapy.
Keywords: BCL2; MRP1; breast cancer; chemoresistance; miR-7; pathological complete response.
© 2019 Hong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Linc00518 Contributes to Multidrug Resistance Through Regulating the MiR-199a/MRP1 Axis in Breast Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(1):16-28. doi: 10.1159/000491659. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30001527
-
miR-145 sensitizes breast cancer to doxorubicin by targeting multidrug resistance-associated protein-1.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 13;7(37):59714-59726. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10845. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27487127 Free PMC article.
-
miR-381 overcomes cisplatin resistance in breast cancer by targeting MDR1.Cell Biol Int. 2019 Jan;43(1):12-21. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11071. Cell Biol Int. 2019. PMID: 30444043
-
Differential altered expression of let-7a and miR-205 tumor-suppressor miRNAs in different subtypes of breast cancer under treatment with Taxol.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2018 Jul;27(7):941-945. doi: 10.17219/acem/70745. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 30019863
-
Mir-1307 regulates cisplatin resistance by targeting Mdm4 in breast cancer expressing wild type P53.Thorac Cancer. 2018 Jun;9(6):676-683. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12607. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Thorac Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29697201 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Downregulation of exosomal miR-7-5p promotes breast cancer migration and invasion by targeting RYK and participating in the atypical WNT signalling pathway.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022 Oct 9;27(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00393-x. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36210461 Free PMC article.
-
Nobiletin in Cancer Therapy: How This Plant Derived-Natural Compound Targets Various Oncogene and Onco-Suppressor Pathways.Biomedicines. 2020 May 5;8(5):110. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8050110. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32380783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P2X7 receptor: a critical regulator and potential target for breast cancer.J Mol Med (Berl). 2021 Mar;99(3):349-358. doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02041-x. Epub 2021 Jan 23. J Mol Med (Berl). 2021. PMID: 33486566 Review.
-
Potential miRNAs for miRNA-Based Therapeutics in Breast Cancer.Noncoding RNA. 2020 Jul 13;6(3):29. doi: 10.3390/ncrna6030029. Noncoding RNA. 2020. PMID: 32668603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microribonucleic Acid-15a-5p Alters Adriamycin Resistance in Breast Cancer Cells by Targeting Cell Division Cycle-Associated Protein 4.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Nov 10;13:8425-8434. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S333830. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34785950 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

