Sustainable development for global mental health: a typology and systematic evidence mapping of external actors in low-income and middle-income countries
- PMID: 31908860
- PMCID: PMC6936513
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjgh-2019-001826
Sustainable development for global mental health: a typology and systematic evidence mapping of external actors in low-income and middle-income countries
Abstract
Introduction: Mental disorders account for a substantial burden of disease and costs in low-income and middle-income countries (LMICs), but attract few resources. With LMIC governments often under economic pressure, an understanding of the external funding landscape is urgently needed. This study develops a new typology of external actors in global health adapted for the sustainable development goals (SDGs) era and uses it to systematically map available evidence on external actors in global mental health.
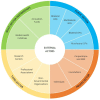
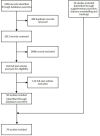
Methods: The new typology was developed in line with conceptualisation in the literature and the SDGs to include 11 types of external actors for health in LMICs. Five databases (EconLit, Embase, Global Health, MEDLINE, PsycINFO) were searched for manuscripts published in peer-reviewed journals in English, French, Italian, Portuguese or Spanish between 1 January 2000 and 31 July 2018 and reporting information on external actors for mental disorders in LMICs. Records were screened by abstract, then full-text against inclusion criteria. Data were extracted and synthesised using narrative analysis.
Results: 79 studies were included in the final review. Five were quantitative studies analysing the resource flow of development assistance for mental health globally over the last two decades. The remainder were qualitative studies providing a description of external actors: the majority of them were published in the last decade, focused on Africa, and on public sector (bilateral and multilateral governmental organisations) and third sector organisations (non-governmental organisations). Evidence was particularly scarce for for-profit organisations and individual households.
Conclusion: This study reveals opportunities for unlocking additional funding for global mental health in the SDG-era from an ecosystem of external actors, and highlights the need to coordinate efforts and to use sustainable, ethical approaches to disbursements. Further research is needed to understand all external actors and the allocation of their contributions in different settings.
Keywords: external actors; global mental health; low-income and middle-income countries; sustainable development; systematic review; typology.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Collaborative Network Global burden of disease study 2017 (GBD 2017) results, 2019. Available: http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool
-
- World Health Organization Mental health atlas 2017. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2018.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
