Efficient Rapid Access to Biginelli for the Multicomponent Synthesis of 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydropyrimidines in Room-Temperature Diisopropyl Ethyl Ammonium Acetate
- PMID: 31909314
- PMCID: PMC6941212
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.9b02286
Efficient Rapid Access to Biginelli for the Multicomponent Synthesis of 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydropyrimidines in Room-Temperature Diisopropyl Ethyl Ammonium Acetate
Abstract
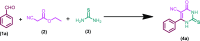
The diisopropyl ethyl ammonium acetate (DIPEAc)-promoted Biginelli protocol has been developed for the first time by a successive one-pot three-component reaction of aldehydes, ethylcyanoacetate/ethyl acetoacetate, and thiourea/urea to afford pharmacologically promising 1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidines in high yields at room temperature. The key benefits of the present scheme are the capability to allow a variability of functional groups, short reaction times, easy workup, high yields, recyclability of the catalyst, and solvent-free conditions, thus providing economic and environmental advantages. In addition, a series of 4-oxo-6-aryl-2-thioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-5-carbonitriles analogues were synthesized and selected for their in vitro antifungal and antibacterial activities.
Copyright © 2019 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
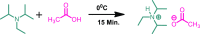





Similar articles
-
Catalytic role in Biginelli reaction: Synthesis and biological property studies of 2-oxo/thioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidines.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2023 Jun;356(6):e2300008. doi: 10.1002/ardp.202300008. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2023. PMID: 36899497 Review.
-
Vanillic aldehydes for the one-pot synthesis of novel 2-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidines.Mol Divers. 2016 Aug;20(3):591-604. doi: 10.1007/s11030-016-9658-y. Epub 2016 Jan 30. Mol Divers. 2016. PMID: 26829937
-
Synthesis of Dihydropyrimidinones (DHPMs) and Hexahydro Xanthene Catalyzed by 1,4-Diazabicyclo [2.2.2] Octane Triflate Under Solvent-Free Condition.Curr Org Synth. 2019;16(5):776-786. doi: 10.2174/1570179415666181113154232. Curr Org Synth. 2019. PMID: 31984893
-
Rapid Construction of Substituted Dihydrothiophene Ureidoformamides at Room Temperature Using Diisopropyl Ethyl Ammonium Acetate: A Green Perspective.ACS Omega. 2020 Nov 5;5(45):29055-29067. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03575. eCollection 2020 Nov 17. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 33225136 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in asymmetric Biginelli reaction.Mol Divers. 2013 May;17(2):389-407. doi: 10.1007/s11030-013-9439-9. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Mol Divers. 2013. PMID: 23588897 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of 3,4-Dihydropyrimidin(thio)one Containing Scaffold: Biginelli-like Reactions.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jul 30;15(8):948. doi: 10.3390/ph15080948. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triethylammonium Hydrogen Sulfate [Et3NH][HSO4]-Catalyzed Rapid and Efficient Multicomponent Synthesis of Pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine and Pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine Hybrids.ACS Omega. 2021 Jul 2;6(28):18215-18225. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c02093. eCollection 2021 Jul 20. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34308052 Free PMC article.
-
Biginelli Reaction Mediated Synthesis of Antimicrobial Pyrimidine Derivatives and Their Therapeutic Properties.Molecules. 2021 Oct 4;26(19):6022. doi: 10.3390/molecules26196022. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Important is the Metal-free Catalytic Knoevenagel Reaction in Medicinal Chemistry? An Updated Review.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(27):4286-4311. doi: 10.2174/0109298673260463231122074253. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38243980 Review.
-
Sulfamic acid pyromellitic diamide-functionalized MCM-41 as a multifunctional hybrid catalyst for melting-assisted solvent-free synthesis of bioactive 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2-(1H)-ones.Sci Rep. 2021 May 27;11(1):11199. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89572-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34045484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Welton T. Ionic Liquids in Green Chemistry. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 225.10.1039/c0gc90047h. - DOI
-
- Wang C.; Guo L.; Li H.; Wang Y.; Weng J.; Wu L. Preparation of Simple Ammonium Ionic Liquids and Their Application in the Cracking of Dialkoxypropanes. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 603–607. 10.1039/b600041j. - DOI
-
- Wang C.; Zhao W.; Li H.; Guo L. Solvent-Free Synthesis of Unsaturated Ketones by the Saucy-Marbet Reaction Using Simple Ammonium Ionic Liquid as a Catalyst. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 843–847. 10.1039/b900042a. - DOI
-
- Weng J.; Wang C.; Li H.; Wang Y. Novel Quaternary Ammonium Ionic Liquids and Their Use as Dual Solvent-Catalysts in the Hydrolytic Reaction. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 96–99. 10.1039/b508325g. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

