Bioluminescent Antibodies through Photoconjugation of Protein G-Luciferase Fusion Proteins
- PMID: 31909607
- PMCID: PMC7086395
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00804
Bioluminescent Antibodies through Photoconjugation of Protein G-Luciferase Fusion Proteins
Abstract
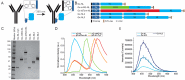
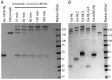
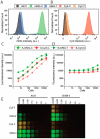
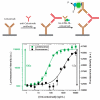
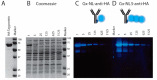
Bioluminescent antibodies represent attractive detection agents in both bioanalytical assays and imaging. Currently, their preparation relies on genetic fusion of luciferases to antibodies or nonspecific chemical conjugation strategies. Here, we report a generic method to generate well-defined covalent antibody-luciferase conjugates starting from commercially available monoclonal antibodies. Our approach uses fusion proteins consisting of the bright blue light-emitting luciferase NanoLuc (NL) and an Fc-binding protein domain (Gx) that can be photo-cross-linked to the antibody using UV light illumination. Green and red color variants were constructed by tight fusion of the NanoLuc with a green fluorescent acceptor domain and introduction of Cy3, respectively. To increase the already bright NanoLuc emission, tandem fusions were successfully developed in which the Gx domain is fused to two or three copies of the NanoLuc domain. The Gx-NL fusion proteins can be efficiently photo-cross-linked to all human immunoglobulin G (IgG) isotypes and most mammalian IgG's using 365 nm light, yielding antibodies with either one or two luciferase domains. The bioluminescent antibodies were successfully used in cell immunostaining and bioanalytical assays such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and Western blotting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Billiald P.; Mousli M.; Goyffon M.; Vaux D. (1997) Engineering of a bioluminescent antigen-binding protein. Biotechnol. Lett. 19, 1037–1041. 10.1023/A:1018463804651. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

