Compartmentalized oskar degradation in the germ plasm safeguards germline development
- PMID: 31909715
- PMCID: PMC6986870
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.49988
Compartmentalized oskar degradation in the germ plasm safeguards germline development
Abstract
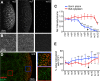
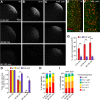
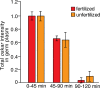
Partitioning of mRNAs into ribonucleoprotein (RNP) granules supports diverse regulatory programs within the crowded cytoplasm. At least two types of RNP granules populate the germ plasm, a cytoplasmic domain at the posterior of the Drosophila oocyte and embryo. Germ granules deliver mRNAs required for germline development to pole cells, the germ cell progenitors. A second type of RNP granule, here named founder granules, contains oskar mRNA, which encodes the germ plasm organizer. Whereas oskar mRNA is essential for germ plasm assembly during oogenesis, we show that it is toxic to pole cells. Founder granules mediate compartmentalized degradation of oskar during embryogenesis to minimize its inheritance by pole cells. Degradation of oskar in founder granules is temporally and mechanistically distinct from degradation of oskar and other mRNAs during the maternal-to-zygotic transition. Our results show how compartmentalization in RNP granules differentially controls fates of mRNAs localized within the same cytoplasmic domain.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; RNA granule; developmental biology; founder granule; germ plasm; mRNA degradation; oskar; ribonucleoprotein.
© 2020, Eichler et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CE, AH, BH, EG No competing interests declared
Figures






Similar articles
-
A late phase of germ plasm accumulation during Drosophila oogenesis requires lost and rumpelstiltskin.Development. 2011 Aug;138(16):3431-40. doi: 10.1242/dev.065029. Epub 2011 Jul 13. Development. 2011. PMID: 21752933 Free PMC article.
-
Stochastic Seeding Coupled with mRNA Self-Recruitment Generates Heterogeneous Drosophila Germ Granules.Curr Biol. 2018 Jun 18;28(12):1872-1881.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.04.037. Epub 2018 May 31. Curr Biol. 2018. PMID: 29861136 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence-dependent but not sequence-specific piRNA adhesion traps mRNAs to the germ plasm.Nature. 2016 Mar 17;531(7594):390-394. doi: 10.1038/nature17150. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Nature. 2016. PMID: 26950602 Free PMC article.
-
Germ granules in Drosophila.Traffic. 2019 Sep;20(9):650-660. doi: 10.1111/tra.12674. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Traffic. 2019. PMID: 31218815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Germ Plasm Biogenesis--An Oskar-Centric Perspective.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2016;116:679-707. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.11.024. Epub 2016 Feb 13. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 26970648 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Caenorhabditis elegans germ granules accumulate hundreds of low translation mRNAs with no systematic preference for germ cell fate regulators.Development. 2024 Jul 1;151(13):dev202575. doi: 10.1242/dev.202575. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Development. 2024. PMID: 38984542 Free PMC article.
-
Germ granules in development.Development. 2023 Jan 15;150(2):dev201037. doi: 10.1242/dev.201037. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Development. 2023. PMID: 36715566 Free PMC article.
-
P-body-like condensates in the germline.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Apr;157:24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2023.06.010. Epub 2023 Jul 3. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 37407370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel structure and composition of the unusually large germline determinant of the wasp Nasonia vitripennis.Mol Biol Cell. 2025 May 1;36(5):ar55. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E24-11-0499. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2025. PMID: 40072502
-
Computational modeling offers new insight into Drosophila germ granule development.Biophys J. 2022 Apr 19;121(8):1465-1482. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.03.014. Epub 2022 Mar 12. Biophys J. 2022. PMID: 35288123 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barckmann B, Pierson S, Dufourt J, Papin C, Armenise C, Port F, Grentzinger T, Chambeyron S, Baronian G, Desvignes J-P, Curk T, Simonelig M. Aubergine iCLIP reveals piRNA-Dependent decay of mRNAs involved in germ cell development in the early embryo. Cell Reports. 2015;12:1205–1216. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.07.030. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

