A pre-clinical validation plan to evaluate analytical sensitivities of molecular diagnostics such as BD MAX MDR-TB, Xpert MTB/Rif Ultra and FluoroType MTB
- PMID: 31910223
- PMCID: PMC6946130
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227215
A pre-clinical validation plan to evaluate analytical sensitivities of molecular diagnostics such as BD MAX MDR-TB, Xpert MTB/Rif Ultra and FluoroType MTB
Abstract
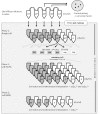
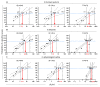
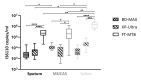
Rapid diagnosis of tuberculosis (TB) and antibiotic resistances are imperative to initiate effective treatment and to stop transmission of the disease. A new generation of more sensitive, automated molecular TB diagnostic tests has been recently launched giving microbiologists more choice between several assays with the potential to detect resistance markers for rifampicin and isoniazid. In this study, we determined analytical sensitivities as 95% limits of detection (LoD95) for Xpert MTB/Rif Ultra (XP-Ultra) and BD-MAX MDR-TB (BD-MAX) as two representatives of the new test generation, in comparison to the conventional FluoroType MTB (FT-MTB). Test matrices used were physiological saline solution, human and a mucin-based artificial sputum (MUCAS) each spiked with Mycobacterium tuberculosis in declining culture- and qPCR-controlled concentrations. With BD-MAX, XP-Ultra, and FT-MTB, we measured LoD95TB values of 2.1 cfu/ml (CI95%: 0.9-23.3), 3.1 cfu/ml (CI95%: 1.2-88.9), and 52.1 cfu/ml (CI95%: 16.7-664.4) in human sputum; of 6.3 cfu/ml (CI95%: 2.9-31.8), 1.5 cfu/ml (CI95%: 0.7-5.0), and 30.4 cfu/ml (CI95%: 17.4-60.7) in MUCAS; and of 2.3 cfu/ml (CI95%: 1.1-12.0), 11.5 cfu/ml (CI95%: 5.6-47.3), and 129.1 cfu/ml (CI95%: 82.8-273.8) in saline solution, respectively. LoD95 of resistance markers were 9 to 48 times higher compared to LoD95TB. BD-MAX and XP-Ultra have an equal and significantly increased analytical sensitivity compared to conventional tests. MUCAS resembled human sputum, while both yielded significantly different results than normal saline. MUCAS proved to be suitable for quality control of PCR assays for TB diagnostics.
Conflict of interest statement
Xpert cartridges, FluoroType reagents and diarella MTB/NTM/MAC qPCR kits were provided free of charge by Cepheid, Hain Lifescience GmbH and gerbion GmbH & Co. KG, respectively. The BD-MAX machine was provided by Becton Dickinson free of charge. MB received a salary from BD for giving a talk at a conference (REMMDI, 11-April-2019). Gerbion GmbH & Co. KG and IML red GmbH are partners in further research projects (TB-Tube and TB-SeqDisK). A patent named “ARTIFICIAL SPUTUM, METHOD OF PRODUCING AN ARTIFICIAL SPUTUM” is submitted in the name of IML red GmbH to the European Patent Office and currently pending (application number EP19165015.9). The patent will not be published before the 25th of September 2020. Commercial affiliations and the pending patent do not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Global tuberculosis report 2018. In: WHO [Internet]. 2018 [cited 22 Feb 2019]. Available: http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

