64Cu-ATSM Positron Emission Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Hypoxia in Human Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 31910670
- PMCID: PMC7328725
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.119.009791
64Cu-ATSM Positron Emission Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Hypoxia in Human Atherosclerosis
Keywords: atherosclerosis; carotid arteries; hypoxia; jugular veins; macrophage.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES
There is no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
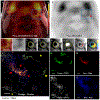
References
-
- Sluimer JC, Gasc JM, van Wanroij JL, Kisters N, Groeneweg M, Sollewijn Gelpke MD, Cleutjens JP, van den Akker LH, Corvol P, Wouters BG, et al. Hypoxia, hypoxia-inducible transcription factor, and macrophages in human atherosclerotic plaques are correlated with intraplaque angiogenesis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51:1258–65. - PubMed
-
- Fujibayashi Y, Taniuchi H, Yonekura Y, Ohtani H, Konishi J and Yokoyama A. Copper-62-ATSM: a new hypoxia imaging agent with high membrane permeability and low redox potential. J Nucl Med. 1997;38:1155–60. - PubMed
-
- Gaens ME, Backes WH, Rozel S, Lipperts M, Sanders SN, Jaspers K, Cleutjens JP, Sluimer JC, Heeneman S, Daemen MJ, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging of carotid atherosclerotic plaque: model selection, reproducibility, and validation. Radiology. 2013;266:271–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

