In the aftermath of clozapine discontinuation: comparative effectiveness and safety of antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia who discontinue clozapine
- PMID: 31910911
- PMCID: PMC7511905
- DOI: 10.1192/bjp.2019.267
In the aftermath of clozapine discontinuation: comparative effectiveness and safety of antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia who discontinue clozapine
Abstract
Background: Although clozapine is often discontinued, there is a paucity of guidelines and evidence on treatment options after clozapine discontinuation. Moreover, it is currently unknown whether reinstating clozapine in patients formerly using clozapine should be avoided.
Aims: To compare the real-world effectiveness of antipsychotics after clozapine cessation.
Method: From Finnish registry data (1995-2017), we identified 2250 patients with schizophrenia who had been using clozapine for ≥1 year before treatment cessation. The primary analysis consisted of adjusted within-individual analyses of psychiatric ward readmission owing to psychosis and treatment failure. Secondary analyses concerned between-individual mortality differences.
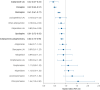
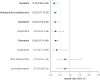
Results: Compared with no use of antipsychotics, risk of psychiatric ward readmission was lowest for reinitiation of clozapine (adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) 0.49; 95% CI 0.40-0.61; P < 0.0001), oral olanzapine (aHR 0.58; 95% CI 0.48-0.71; P < 0.0001) and antipsychotic polypharmacy (aHR 0.62; 95% CI 0.53-0.72; P < 0.0001). Risk of treatment failure was lowest for aripiprazole long acting injectable (aHR 0.42; 95% CI 0.27-0.65; P < 0.0001), reinitiation of clozapine (aHR 0.49; 95% CI 0.43-0.57; P < 0.0001) and oral olanzapine (aHR 0.69; 95% CI 0.61-0.77; P < 0.0001). Mortality risk was lowest for reinitiation of clozapine (aHR 0.18; 95% CI 0.09-0.36; P < 0.0001) and oral olanzapine (aHR 0.26; 95% CI 0.17-0.40; P < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Clozapine and olanzapine are the most effective and safest treatment options in those discontinuing clozapine for undefined reasons. Clozapine should therefore be reconsidered in patients with schizophrenia who previously discontinued this compound.
Keywords: Schizophrenia; antipsychotics; clozapine; discontinuation; psychiatric ward readmission.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Leucht S, Cipriani A, Spineli L, Mavridis D, Örey D, Richter F, et al. Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet 2013; 382(9896): 951–62. - PubMed
-
- Siskind D, McCartney L, Goldschlager R, Kisely S. Clozapine v. first- and second-generation antipsychotics in treatment-refractory schizophrenia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry 2016; 209(5): 385–92. - PubMed
-
- Land R, Siskind D, McArdle P, Kisely S, Winckel K, Hollingworth SA. The impact of clozapine on hospital use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr Scand 2017; 135(4): 296–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

