Diversification of Campylobacter jejuni Flagellar C-Ring Composition Impacts Its Structure and Function in Motility, Flagellar Assembly, and Cellular Processes
- PMID: 31911488
- PMCID: PMC6946799
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.02286-19
Diversification of Campylobacter jejuni Flagellar C-Ring Composition Impacts Its Structure and Function in Motility, Flagellar Assembly, and Cellular Processes
Abstract
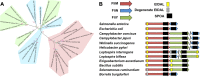
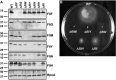
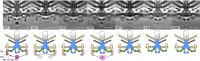
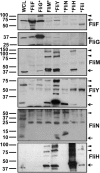
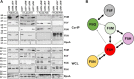
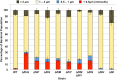
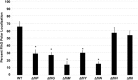
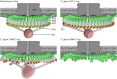
Bacterial flagella are reversible rotary motors that rotate external filaments for bacterial propulsion. Some flagellar motors have diversified by recruiting additional components that influence torque and rotation, but little is known about the possible diversification and evolution of core motor components. The mechanistic core of flagella is the cytoplasmic C ring, which functions as a rotor, directional switch, and assembly platform for the flagellar type III secretion system (fT3SS) ATPase. The C ring is composed of a ring of FliG proteins and a helical ring of surface presentation of antigen (SPOA) domains from the switch proteins FliM and one of two usually mutually exclusive paralogs, FliN or FliY. We investigated the composition, architecture, and function of the C ring of Campylobacter jejuni, which encodes FliG, FliM, and both FliY and FliN by a variety of interrogative approaches. We discovered a diversified C. jejuni C ring containing FliG, FliM, and both FliY, which functions as a classical FliN-like protein for flagellar assembly, and FliN, which has neofunctionalized into a structural role. Specific protein interactions drive the formation of a more complex heterooligomeric C. jejuni C-ring structure. We discovered that this complex C ring has additional cellular functions in polarly localizing FlhG for numerical regulation of flagellar biogenesis and spatial regulation of division. Furthermore, mutation of the C. jejuni C ring revealed a T3SS that was less dependent on its ATPase complex for assembly than were other systems. Our results highlight considerable evolved flagellar diversity that impacts motor output, biogenesis, and cellular processes in different species.IMPORTANCE The conserved core of bacterial flagellar motors reflects a shared evolutionary history that preserves the mechanisms essential for flagellar assembly, rotation, and directional switching. In this work, we describe an expanded and diversified set of core components in the Campylobacter jejuni flagellar C ring, the mechanistic core of the motor. Our work provides insight into how usually conserved core components may have diversified by gene duplication, enabling a division of labor of the ancestral protein between the two new proteins, acquisition of new roles in flagellar assembly and motility, and expansion of the function of the flagellum beyond motility, including spatial regulation of cell division and numerical control of flagellar biogenesis in C. jejuni Our results highlight that relatively small changes, such as gene duplications, can have substantial ramifications on the cellular roles of a molecular machine.
Keywords: C ring; FlhG; FliI; FliN; FliY; flagellar motor; polar flagella; type III secretion.
Copyright © 2020 Henderson et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Three SpoA-domain proteins interact in the creation of the flagellar type III secretion system in Helicobacter pylori.J Biol Chem. 2018 Sep 7;293(36):13961-13973. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002263. Epub 2018 Jul 10. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29991595 Free PMC article.
-
A Polar Flagellar Transcriptional Program Mediated by Diverse Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems and Basal Flagellar Proteins Is Broadly Conserved in Polar Flagellates.mBio. 2020 Mar 3;11(2):e03107-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03107-19. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32127455 Free PMC article.
-
Polar flagellar biosynthesis and a regulator of flagellar number influence spatial parameters of cell division in Campylobacter jejuni.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Dec;7(12):e1002420. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002420. Epub 2011 Dec 1. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 22144902 Free PMC article.
-
Directional Switching Mechanism of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019 Jul 31;17:1075-1081. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.07.020. eCollection 2019. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 31452860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and function of the bi-directional bacterial flagellar motor.Biomolecules. 2014 Feb 18;4(1):217-34. doi: 10.3390/biom4010217. Biomolecules. 2014. PMID: 24970213 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
FliO is an evolutionarily conserved yet diversified core component of the bacterial flagellar type III secretion system.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 6:2025.05.06.652439. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.06.652439. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Aug 26;122(34):e2512476122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2512476122. PMID: 40654941 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The Architectural Dynamics of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Switch.Biomolecules. 2020 May 29;10(6):833. doi: 10.3390/biom10060833. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32486003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A flagellar accessory protein links chemotaxis to surface sensing.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 20:2024.06.20.599946. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.20.599946. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Bacteriol. 2024 Nov 21;206(11):e0040424. doi: 10.1128/jb.00404-24. PMID: 38948737 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Viscosity-dependent determinants of Campylobacter jejuni impacting the velocity of flagellar motility.mBio. 2024 Jan 16;15(1):e0254423. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02544-23. Epub 2023 Dec 12. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38085029 Free PMC article.
-
Campylobacter jejuni virulence factors: update on emerging issues and trends.J Biomed Sci. 2024 May 1;31(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01033-6. J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 38693534 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

