Retroperitoneal Liposarcoma with Multilocular Cysts
- PMID: 31911764
- PMCID: PMC6940463
- DOI: 10.1159/000504695
Retroperitoneal Liposarcoma with Multilocular Cysts
Abstract
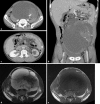
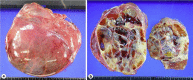
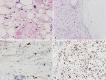
In this study, we describe a 60-year-old man with a giant retroperitoneal liposarcoma with multilocular cysts. He was admitted to our hospital because of a 5-month history of abdominal distention. Abdominal computed tomography revealed a giant lobulated cystic mass occupying the retroperitoneal space that contained partially solid fat components. Magnetic resonance imaging indicated that this complex mass exhibited a low signal intensity on a T1-weighted image, whereas it exhibited a high and focally intermediate signal intensity on a T2-weighted image. This patient was diagnosed with a mucinous type of retroperitoneal sarcoma, which was then resected. During surgery, the tumor was isolated from the retroperitoneum and other organs, but the detachment was required only because of fixation around the left external iliac artery. The histological diagnosis was a well-differentiated liposarcoma with multilocular cysts that contained old bloody, serous, and mucinous fluids, which are a rare phenomenon in liposarcoma. This case indicates that retroperitoneal liposarcoma should also be considered as a differential diagnosis of retroperitoneal cystic mass.
Keywords: Liposarcoma; Multilocular cysts; Retroperitoneum.
Copyright © 2019 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Goldblum JR, Weiss SW, Folpe AL. Enziger and Weiss's soft tissue tumors. 6th ed. Philadelphia: ElsevierHealth Sciences; 2013. Liposarcoma; pp. pp. 484–523.
-
- Horiguchi A, Oyama M. [Perinephric liposarcoma mimicking cystic renal tumor] Nippon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi. 2002 Mar;93((3)):491–4. - PubMed
-
- Uchihashi K, Matsuyama A, Shiba E, Kimura Y, Ogata T, Yabuki K, et al. Retroperitoneal dedifferentiated liposarcoma with huge cystic degeneration: A case report. Pathol Int. 2017 May;67((5)):264–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

