Inter-country variability over time in the mortality of mechanically ventilated patients
- PMID: 31912203
- PMCID: PMC7222132
- DOI: 10.1007/s00134-019-05867-9
Inter-country variability over time in the mortality of mechanically ventilated patients
Abstract
Purpose: Variations in clinical characteristics and management and in the mortality of mechanically ventilated patients have not been sufficiently evaluated. We hypothesized that mortality shows a variability associated with country after adjustment for clinical characteristics and management.
Methods: Analysis of four studies carried out at 6-year intervals over an 18-year period. The studies included 26,024 patients (5183 in 1998, 4968 in 2004, 8108 in 2010, and 7765 in 2016) admitted to 1253 units from 38 countries. The primary outcome was 28-day mortality. We performed analyses using multilevel logistic modeling with mixed-random effects, including country as a random variable. To evaluate the effect of management strategies on mortality, a mediation analysis was performed.
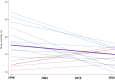
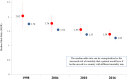
Results: Adjusted 28-day mortality decreased significantly over time (first study as reference): 2004: odds ratio 0.82 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.72-0.93); 2010: 0.63 (95% CI 0.53-0.75); 2016: 0.49 (95% CI 0.39-0.61). A protective ventilatory strategy and the use of continuous sedation mediated a moderate fraction of the effect of time on mortality in patients with moderate hypoxemia and without hypoxemia, respectively. Logistic multilevel modeling showed a significant effect of country on mortality: median odds ratio (MOR) in 1998: 2.02 (95% CI 1.57-2.48); in 2004: 1.76 (95% CI 1.47-2.06); in 2010: 1.55 (95% CI 1.37-1.74), and in 2016: 1.39 (95% CI 1.25-1.54).
Conclusions: These findings suggest that country could contribute, independently of confounder variables, to outcome. The magnitude of the effect of country decreased over time. Clinical trials registered with http://www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT02731898).
Keywords: Epidemiology; Mechanical ventilation; Mortality; Outcome; Variability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Jaber S, Lescot T, Futier E, Paugam-Burtz C, Seguin P, Ferrandiere M, Lasocki S, Mimoz O, Hengy B, Sannini A, Pottecher J, Abback PS, Riu B, Belafia F, Constantin JM, Masseret E, Beaussier M, Verzilli D, De Jong A, Chanques G, Brochard L, Molinari N. Effect of noninvasive ventilation on tracheal reintubation among patients with hypoxemic respiratory failure following abdominal surgery: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;315:1345–1353. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.2706. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lemiale V, Mokart D, Resche-Rigon M, Pène F, Mayaux J, Faucher E, Nyunga M, Girault C, Perez P, Guitton C, Ekpe K, Kouatchet A, Théodose I, Benoit D, Canet E, Barbier F, Rabbat A, Bruneel F, Vincent F, Klouche K, Loay K, Mariotte E, Bouadma L, Moreau AS, Seguin A, Meert AP, Reignier J, Papazian L, Mehzari I, Cohen Y, Schenck M, Hamidfar R, Darmon M, Demoule A, Chevret S, Azoulay E. Effect of noninvasive ventilation vs oxygen therapy on mortality among immunocompromised patients with acute respiratory failure: a randomized clinical Trial. JAMA. 2015;314:1711–1719. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.12402. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Demoule A, Chevret S, Carlucci A, Kouatchet A, Jaber S, Meziani F, Schmidt M, Schnell D, Clergue C, Aboab J, Rabbat A, Eon B, Guérin C, Georges H, Zuber B, Dellamonica J, Das V, Cousson J, Perez D, Brochard L, Azoulay E. Changing use of noninvasive ventilation in critically ill patients: trends over 15 years in francophone countries. Intensive Care Med. 2016;42:82–92. doi: 10.1007/s00134-015-4087-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Serpa Neto A, Cardoso SO, Manetta JA, Pereira VG, Espósito DC, de Pasqualucci M, Damasceno MC, Schultz MJ. Association between use of lung-protective ventilation with lower tidal volumes and clinical outcomes among patients without acute respiratory distress syndrome: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2012;308:1651–1659. doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.13730. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Writing Group for the PReVENT Investigators. Simonis FD, Serpa Neto A, Binnekade JM, Braber A, Bruin KCM, Determann RM, Goekoop GJ, Heidt J, Horn J, Innemee G, de Jonge E, Juffermans NP, Spronk PE, Steuten LM, Tuinman PR, de Wilde RBP, Vriends M, Gama de Abreu M, Pelosi P, Schultz MJ. Effect of a low vs intermediate tidal volume strategy on ventilator-free days in intensive care unit patients without ARDS: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2018;320:1872–1880. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.14280. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

