Primary sarcoma of the cervix: an analysis of patient and tumor characteristics, treatment patterns, and outcomes
- PMID: 31912680
- PMCID: PMC7189069
- DOI: 10.3802/jgo.2020.31.e25
Primary sarcoma of the cervix: an analysis of patient and tumor characteristics, treatment patterns, and outcomes
Abstract
Objective: Primary sarcoma of the cervix is rare and is associated with worse outcomes as compared to other histologies. The purpose of this study was to identify national treatment patterns and outcomes based on histological subtype using the National Cancer Database (NCDB).
Methods: The NCDB was queried for patients with cervical cancer from 2004-2015. Clinico-demographic treatment details were obtained and compared between patients with squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), adenocarcinoma, and sarcoma of the cervix. Multivariable Cox regression and the Kaplan-Meier method was used to examine survival.
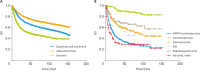
Results: 107,177 patients met inclusion criteria including 81,245 (75.8%) women with SCC, 24,562 (22.9%) women with adenocarcinoma, and 1,370 (1.3%) women with sarcoma. Of the patients with cervical sarcoma, 680 (49.6%) patients had carcinosarcoma or malignant mixed Müllerian tumor, 255 (18.6%) patients had leiomyosarcoma, 197 (14.4%) patients had adenosarcoma, 28 (2.0%) patients had endometrial stromal sarcoma (ESS), 85 (6.2%) patients had rhabdomyosarcoma, and 125 (9.1%) patients had sarcoma not otherwise specified (NOS). Patients with sarcoma were older and more likely to be treated primarily with surgery. On multivariable Cox regression, sarcoma had decreased overall survival (OS) as compared to patients with SCC (hazard ratio=2.17; 95% CI=1.99-2.37; p<0.001). Among patients with sarcoma, 5-year OS was 89.2% for adenosarcoma, 66.2% for rhabdomyosarcoma, 55.6% for leiomyosarcoma, 45.8% for ESS, 31.6% for carcinosarcoma, and 29.2% for sarcoma NOS.
Conclusions: Primary cervical sarcomas have inferior outcomes compared to SCC and adenocarcinoma. Sarcoma NOS and carcinosarcoma have the worst prognosis among sarcoma subtypes.
Keywords: Cervix; Sarcoma.
Copyright © 2020. Asian Society of Gynecologic Oncology, Korean Society of Gynecologic Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Wang SS, Sherman ME, Hildesheim A, Lacey JV, Jr, Devesa S. Cervical adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma incidence trends among white women and black women in the United States for 1976–2000. Cancer. 2004;100:1035–1044. - PubMed
-
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for cervical cancer: recommendations and rationale. Am J Nurs. 2003;103:101–102. 105–106, 108–109. - PubMed
-
- Wright JD, Rosenblum K, Huettner PC, Mutch DG, Rader JS, Powell MA, et al. Cervical sarcomas: an analysis of incidence and outcome. Gynecol Oncol. 2005;99:348–351. - PubMed
-
- Bansal S, Lewin SN, Burke WM, Deutsch I, Sun X, Herzog TJ, et al. Sarcoma of the cervix: natural history and outcomes. Gynecol Oncol. 2010;118:134–138. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

