Estimating Serotype-specific Efficacy of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines Using Hierarchical Models
- PMID: 31913908
- PMCID: PMC7508209
- DOI: 10.1097/EDE.0000000000001135
Estimating Serotype-specific Efficacy of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines Using Hierarchical Models
Abstract
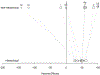
Pneumococcal conjugate vaccines target 10 or 13 specific serotypes. To evaluate the overall efficacy of these products, the vaccine-targeted serotypes are typically aggregated into a single group. However, it is often desirable to evaluate variations in effects for different serotypes. These serotype-specific estimates are often based on small counts, resulting in a high degree of uncertainty (i.e., large standard errors and wide confidence intervals). An alternative is to use a hierarchical Bayesian statistical model, which estimates overall effectiveness while simultaneously providing estimates of serotype-specific vaccine effects. These shrunken serotype-specific estimators often have smaller mean squared errors (MSEs) than unbiased versions due to a large decrease in posterior uncertainty. We reanalyzed published data from a randomized controlled trial on the efficacy of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) against community-acquired pneumonia caused by vaccine-targeted serotype using a hierarchical model. This model provides a potential framework for obtaining estimates of serotype-specific vaccine effects with reduced MSEs.
Figures

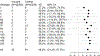
Similar articles
-
A post-hoc analysis of serotype-specific vaccine efficacy of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine against clinical community acquired pneumonia from a randomized clinical trial in the Netherlands.Vaccine. 2019 Jul 9;37(30):4147-4154. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.05.065. Epub 2019 May 31. Vaccine. 2019. PMID: 31155413 Clinical Trial.
-
The impact of 10-valent and 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines on serotype 19A invasive pneumococcal disease.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2015;14(10):1359-66. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2015.1075884. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2015. PMID: 26289973 Review.
-
Impact of pneumococcal vaccination in children on serotype distribution in adult community-acquired pneumonia using the serotype-specific multiplex urinary antigen detection assay.Vaccine. 2016 Apr 29;34(20):2342-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.03.052. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 27016653
-
Impact of the pediatric 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on serotype distribution and clinical characteristics of pneumococcal pneumonia in adults: The Japan Pneumococcal Vaccine Effectiveness Study (J-PAVE).Vaccine. 2019 May 6;37(20):2687-2693. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.04.009. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Vaccine. 2019. PMID: 30975569
-
Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine against serotype 3 pneumococcal pneumonia in adults: A systematic review and pooled analysis.Vaccine. 2019 Oct 8;37(43):6310-6316. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.08.059. Epub 2019 Sep 12. Vaccine. 2019. PMID: 31522807
Cited by
-
Estimating the Serotype-Specific Association Between the Concentration of Vaccine-Induced Serum Antibodies and Protection Against Pneumococcal Colonization.J Infect Dis. 2025 Jul 30;232(1):e27-e34. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaf106. J Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40036886 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine Impact on Serotype 3: A Review of Surveillance Data.Infect Dis Ther. 2021 Mar;10(1):521-539. doi: 10.1007/s40121-021-00406-w. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Infect Dis Ther. 2021. PMID: 33587245 Free PMC article.
-
PCV13 Vaccination of Adults against Pneumococcal Disease: What We Have Learned from the Community-Acquired Pneumonia Immunization Trial in Adults (CAPiTA).Microorganisms. 2022 Jan 8;10(1):127. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10010127. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35056576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating post-vaccine expansion patterns of pneumococcal serotypes.Vaccine. 2020 Nov 17;38(49):7756-7763. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.10.045. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Vaccine. 2020. PMID: 33164799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonten M, Bolkenbaas M, Huijts S, Webber C, Gault S, Gruber W, Grobee D, Team CS: Community-acquired pneumonia immunization trial in adults-CAPiTA In: International Symposium on Pneumococci and Pneumococccal Diseases 9: 2014; Hyderabad, India.
-
- Fleming-Dutra KE, Conklin L, Loo JD, Knoll MD, Park DE, Kirk J, Goldblatt D, Whitney CG, O’Brien KL: Systematic Review of the Effect of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine Dosing Schedules on Vaccine-type Nasopharyngeal Carriage . Pediatr Infect Dis J 2014, 33(Suppl 2 Optimum Dosing of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine For Infants 0 A Landscape Analysis of Evidence Supportin g Different Schedules):S152–S160. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pilishvili T: 13-valent pneumoococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) effects on disease caused by serotype 3. In: Advisory Committee on Immunization Praactices: February 28, 2019; Atlanta, GA 2019.
-
- Andrews NJ, Waight PA, Burbidge P, Pearce E, Roalfe L, Zancolli M, Slack M, Ladhani SN, Miller E, Goldblatt D: Serotype-specific effectiveness and correlates of protection for the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine: a postlicensure indirect cohort study. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2014, 14(9):839–846. - PubMed
-
- Bonten MJM, Huijts SM, Bolkenbaas M, Webber C, Patterson S, Gault S, van Werkhoven CH, van Deursen AMM, Sanders EAM, Verheij TJM et al.: Polysaccharide Conjugate Vaccine against Pneumococcal Pneumonia in Adults. New England Journal of Medicine 2015, 372(12):1114–1125. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

