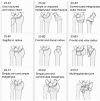
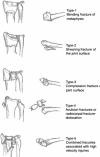
A retrospective evaluation of reliability and reproducibility of Arbeitsgemeinschaftfür Osteosynthesefragen classification and Fernandez classification for distal radius fracture
- PMID: 31914022
- PMCID: PMC6959948
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018508
A retrospective evaluation of reliability and reproducibility of Arbeitsgemeinschaftfür Osteosynthesefragen classification and Fernandez classification for distal radius fracture
Abstract
This is a retrospective evaluated. The objective of this study was to test the interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility of fracture classification with Arbeitsgemeinschaftfür Osteosynthesefragen (AO) system and Fernandez system used by 5 senior orthopedic surgeons.Anteroposterior and lateral radiographs of 160 patients hospitalized for displaced distal radius fracture were examined. Independently, 5 orthopedic surgeons evaluated the radiographs according to 2 different distal radius classification systems (3 types of results). Three statistical tools were used to measure interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility. The intraclass correlation coefficient and kappa coefficient (k) were used to assess both interobserver and intraobserver agreement of AO and Fernandez. Kappa value indicated poor agreement (<0), slight (0-0.20), fair (0.21-0.40), moderate (0.41-0.60), good (0.61-0.80), and perfect (0.81-1.00).The intraobserver reproducibility of AO system (9 types) and Fernandez system were moderate with a value of 0.577 and 0.438. The intraobserver reproducibility of AO system (27 subtypes) was 0.286. The interobserver reliability of AO system (9 types) was moderate with a value of 0.469 and that of Fernandez was moderate with a value of 0.435. The interobserver reliability of AO system (27 subtypes) was 0.299.Neither of the 2 systems can give us a satisfactory agreement between interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility. In AO system, the interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility of the 9 types decreased with the increase of subgroups.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reliability of distal radius fracture classification systems: a CT based study.Emerg Radiol. 2024 Dec;31(6):873-879. doi: 10.1007/s10140-024-02294-2. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Emerg Radiol. 2024. PMID: 39499384
-
Are distal radius fracture classifications reproducible? Intra and interobserver agreement.Sao Paulo Med J. 2008 May 1;126(3):180-5. doi: 10.1590/s1516-31802008000300008. Sao Paulo Med J. 2008. PMID: 18711658 Free PMC article.
-
Classification of distal radius fractures: an analysis of interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility.J Hand Surg Am. 1996 Jul;21(4):574-82. doi: 10.1016/s0363-5023(96)80006-2. J Hand Surg Am. 1996. PMID: 8842946
-
Adult distal radius fractures classification systems: essential clinical knowledge or abstract memory testing?Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2016 Nov;98(8):525-531. doi: 10.1308/rcsann.2016.0237. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2016. PMID: 27513789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrarater and Inter-rater Reliability of Tibial Plateau Fracture Classifications: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.JB JS Open Access. 2024 Oct 3;9(4):e23.00181. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.OA.23.00181. eCollection 2024 Oct-Dec. JB JS Open Access. 2024. PMID: 39364175 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Relation between the dash score and radiographic evaluation of the wrist in patients with wrist fracture.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Mar 15;25(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07307-2. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 38491493 Free PMC article.
-
Standard radiographic assessments of distal radius fractures miss involvement of the distal radioulnar joint: a diagnostic study.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022 Jun;142(6):1075-1082. doi: 10.1007/s00402-021-03801-7. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022. PMID: 33558991 Free PMC article.
-
Validity of classification of distal radial fractures in the Swedish fracture register.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Jun 26;22(1):587. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04473-5. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021. PMID: 34174861 Free PMC article.
-
Temporary external fixation versus direct ORIF in complete displaced intra-articular radius fractures: a prospective comparative study.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022 Dec;48(6):4349-4356. doi: 10.1007/s00068-021-01611-5. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022. PMID: 33630119
-
Evaluation of Intra- and Interobserver Reproducibility of the New AO/OTA Classification for Distal Radius Fractures Compared with the Fernandez Classification.Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2022 Sep 26;57(6):917-923. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1740471. eCollection 2022 Dec. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2022. PMID: 36540737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davis DI, Baratz M. Soft tissue complications of distal radius fractures. Hand Clin 2010;2:229–35. - PubMed
-
- Müller ME, Nazarian S, Koch P. Classification AO Des Fractures: Tome I: Les Os Longs. 1st ed.1987;Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag, Part 2.
-
- Fernandez DL, Jupiter J. Fractures of the Distal Radius: A Practical Approach to Management. New York, NY: Springer Verlag; 1996.
-
- Shrout PE, Fleiss JL. Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull 1979;86:420–8. - PubMed
-
- Naqvi SGA, Reynolds T, Kitsis C. Interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility of the fernandez classification for distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg 2009;34:483–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical