Urinary fatty acid and retinol binding protein-4 predict CKD progression in severe NAFLD patients with hypertension: 4-year study with clinical and experimental approaches
- PMID: 31914044
- PMCID: PMC6959901
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018626
Urinary fatty acid and retinol binding protein-4 predict CKD progression in severe NAFLD patients with hypertension: 4-year study with clinical and experimental approaches
Abstract
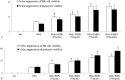
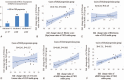
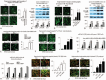
Detection of the chronic kidney disease (CKD) progression can begin early intervention to improve the prognosis of severe non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). This bi-directional cross-sectional study evaluates the roles of fatty acid-binding protein (FABP) and retinol binding protein (RBP4), which are produced from inflamed liver, adipose tissue and immune cells, for the prediction of CKD progression in severe NAFLD. Ninety severe NAFLD patients with hypertension and proteinuria (NAFLDHTN) were enrolled and divided into CKD (n = 39) and non-CKD groups (n = 51). Among 39 NAFLDHTN patients, 18 cases were categorized as CKD progression group. In comparison with CKD stable group (n = 21), the positive correlation between fold change values of hepatic fibrotic score (KPa), urinary FABP4 or urinary RBP4 versus severity of albuminuria were noted among CKD progression group. On multivariate analysis, high body mass index (BMI, >25 kg/m), high hepatic fibrosis score (>9.5 KPa), high urinary level of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1, >2239 μg/g cr), high urinary level of FABP4 (>115 ng/g cr) and high urinary level of RBP4 (>33.5 mg/g cr) are 5 independent predictors for progressive CKD during 24 months of follow-up. Synergetic effect was noted among these 5 risk factors for the prediction of CKD progression in NAFLDHTN patients. The in vitro experiments revealed that both FABP4 and RBP4 directly enhanced albumin-induced ER stress and apoptosis of human renal tubular epithelial cell line HK-2 cells and human podocytes cell lines. Through clinical and experimental approaches, this study revealed new 5 synergetic predictors including high BMI, hepatic fibrosis score, urinary level of VCAM-1, urinary level of FABP4 and RBP4, for the CKD progression in severe NAFLD patients with hypertension and proteinuria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 2004;351:1296–305. - PubMed
-
- Sung KC, Wild SH, Byrne CD. Development of new fatty liver, or resolution of existing fatty liver, over five years of follow-up, and risk of incident hypertension. J Hepatol 2014;60:1040–5. - PubMed
-
- Mantovani A, Zaza G, Byrne CD, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease increases risk of incident chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism 2018;79:64–76. - PubMed
-
- Cottone S, Mulè G, Nardi E, et al. C-reactive protein and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 are stronger predictors of oxidant stress than blood pressure in established hypertension. J Hypertens 2007;25:423–8. - PubMed
-
- Zhang DW, Huang XZ, Wu JH, et al. Effects of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on renal damage in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Ren Fail 2012;34:915–20. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

