Hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning and the role of NADPH oxidase inhibition in postischemic acute kidney injury induced in spontaneously hypertensive rats
- PMID: 31914135
- PMCID: PMC6948727
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226974
Hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning and the role of NADPH oxidase inhibition in postischemic acute kidney injury induced in spontaneously hypertensive rats
Abstract
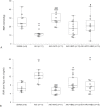
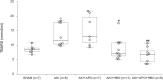
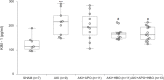
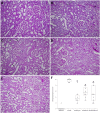
Renal ischemia/reperfusion injury is a common cause of acute kidney injury (AKI) and hypertension might contribute to the increased incidence of AKI. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of single and combined hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) preconditioning and NADPH oxidase inhibition on oxidative stress, kidney function and structure in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) after renal ischemia reperfusion injury. HBO preconditioning was performed by exposing to pure oxygen (2.026 bar) twice a day for two consecutive days for 60 minutes, and 24h before AKI induction. For AKI induction, the right kidney was removed and ischemia was performed by clamping the left renal artery for 45 minutes. NADPH oxidase inhibition was induced by apocynin (40 mg/kg b.m., intravenously) 5 minutes before reperfusion. AKI significantly increased renal vascular resistance and reduced renal blood flow, which were significantly improved after apocynin treatment. Also, HBO preconditioning, with or without apocynin treatment showed improvement on renal hemodynamics. AKI significantly increased plasma creatinine, urea, phosphate levels and lipid peroxidation in plasma. Remarkable improvement, with decrease in creatinine, urea and phosphate levels was observed in all treated groups. HBO preconditioning, solitary or with apocynin treatment decreased lipid peroxidation in plasma caused by AKI induction. Also, combined with apocynin, it increased catalase activity and solitary, glutathione reductase enzyme activity in erythrocytes. While AKI induction significantly increased plasma KIM- 1 levels, HBO preconditioning, solitary or with apocynin decreased its levels. Considering renal morphology, significant morphological alterations present after AKI induction were significantly improved in all treated groups with reduced tubular dilatation, tubular necrosis in the cortico-medullary zone and PAS positive cast formation. Our results reveal that NADPH oxidase inhibition and hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning, with or without NADPH oxidase inhibition may have beneficial effects, but their protective role should be evaluated in further studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hyperbaric Oxygen Preconditioning Upregulates Heme OxyGenase-1 and Anti-Apoptotic Bcl-2 Protein Expression in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats with Induced Postischemic Acute Kidney Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 30;22(3):1382. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031382. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33573145 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperbaric oxygenation protects the kidney against ischemia-reperfusion injury.Undersea Hyperb Med. 2020 First Quarter;47(1):21-30. doi: 10.22462/01.03.2020.3. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2020. PMID: 32176943
-
Immunohistochemical Analysis of 4-HNE, NGAL, and HO-1 Tissue Expression after Apocynin Treatment and HBO Preconditioning in Postischemic Acute Kidney Injury Induced in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jul 22;10(8):1163. doi: 10.3390/antiox10081163. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439411 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of protective strategies against ischemia/reperfusion injury: The role of hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning.Brain Behav. 2018 Mar 30;8(5):e00959. doi: 10.1002/brb3.959. eCollection 2018 May. Brain Behav. 2018. PMID: 29761012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the methoxyphenol apocynin, a vascular NADPH oxidase inhibitor, as a chemopreventative agent in the potential treatment of cardiovascular diseases.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2008 Jul;6(3):204-17. doi: 10.2174/157016108784911984. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18673160 Review.
Cited by
-
Hyperbaric Oxygen Reduces Oxidative Stress Impairment and DNA Damage and Simultaneously Increases HIF-1α in Ischemia-Reperfusion Acute Kidney Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 30;25(7):3870. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073870. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612680 Free PMC article.
-
Natural compounds targeting mitochondrial dysfunction: emerging therapeutics for target organ damage in hypertension.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 15;14:1209890. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1209890. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37397478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding chronic inflammation: couplings between cytokines, ROS, NO, Cai 2+, HIF-1α, Nrf2 and autophagy.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 8;16:1558263. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1558263. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40264757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Blockade and Statins on Kidney Injury Marker 1 (KIM-1) in Female Rats Receiving L-NAME and Angiotensin II.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 30;24(7):6500. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076500. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047470 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Apocynin: A Promising Antioxidant Strategy for Acute Kidney Injury.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Aug 21;14(8):1025. doi: 10.3390/antiox14081025. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40867921 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liano F, Pascual J. Epidemiology of acute renal failure: a prospective, multicenter, community-based study. Madrid Acute Renal Failure Study Group. Kidney Int. 1996;50(3):811–818. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

