LncRNA XIST serves as a ceRNA to regulate the expression of ASF1A, BRWD1M, and PFKFB2 in kidney transplant acute kidney injury via sponging hsa-miR-212-3p and hsa-miR-122-5p
- PMID: 31914881
- PMCID: PMC7028162
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1707454
LncRNA XIST serves as a ceRNA to regulate the expression of ASF1A, BRWD1M, and PFKFB2 in kidney transplant acute kidney injury via sponging hsa-miR-212-3p and hsa-miR-122-5p
Abstract
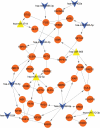
We aimed to identify potential mechanism associated with acute kidney injury (AKI) after kidney transplantation. The dataset GSE53771, which contained 18 zero-hour (ZERO group) and 18 selected post-transplant (POST group) biopsy samples from 18 kidney allografts (8 AKI and 10 controls) was downloaded from GEO database. Differentially expressed miRNAs (DEMIs) were screened using limma package, and bidirectional hierarchical clustering of the DEMIs was performed using the pheatmap package. Target genes of DEMIs were predicted by miRWalk 2.0, miRNA-target genes networks were presented using Cytoscape, protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks were constructed by STRING (version:10.0) database, and competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNA) regulating network were constructed using Cytoscape. In ZERO and POST groups, a total of 4 and 24 differentially expressed miRNAs were obtained in AKI samples compared with control, respectively. Specifically, 71 lncRNAs were obtained to interact with five miRNAs (hsa-miR-215-5p, hsa-miR-192-5p, hsa-miR-422a, hsa-miR-212-3p and hsa-miR-122-5p). Histone chaperone ASF1A (ASF1A) and bromodomain and WD repeat-containing protein 1(BRWD1) were targeted by hsa-miR-212-3p in PPI network. In ceRNA network, lncRNA XIST could interact with four miRNAs (hsa-miR-212-3p, hsa-miR-122-5p, hsa-miR-215-5p, and hsa-miR-192-5p). LncRNA XIST might serve as a ceRNA to sponge hsa-miR-212-3p to regulate the development of AKI via altering the expression of ASF1A/BRWD1. Furthermore, lncRNA XIST could also interact with hsa-miR-122-5p to modulate the expression of PFKFB2 in thyroid hormone signaling pathway and AMPK signaling pathway. LncRNA XIST can serve as a ceRNA to sponge hsa-miR-212-3p and hsa-miR-122-5p to regulate AKI progression via modulating the expression of ASF1A, BRWD1, and PFKFB2.[Figure: see text].
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; competing endogenous RNAs; differentially expressed microRNAs; kidney transplantation; target genes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The miR-15a-5p-XIST-CUL3 regulatory axis is important for sepsis-induced acute kidney injury.Ren Fail. 2019 Nov;41(1):955-966. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2019.1669460. Ren Fail. 2019. PMID: 31658856 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potentially functional circular RNAs hsa_circ_0070934 and hsa_circ_0004315 as prognostic factors of hepatocellular carcinoma by integrated bioinformatics analysis.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 23;12(1):4933. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-08867-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35322101 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Role of miRNAs and lncRNAs in Gout.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Jun 29;2022:6513565. doi: 10.1155/2022/6513565. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9864323. doi: 10.1155/2023/9864323. PMID: 35813414 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
A review on the role of KCNQ1OT1 lncRNA in human disorders.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Mar;255:155188. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155188. Epub 2024 Feb 3. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38330620 Review.
-
Long journey on the role of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) in acute kidney injury (AKI).Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Nov;263:155591. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155591. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 39288476 Review.
Cited by
-
ELK1‑mediated upregulation of lncRNA LBX2‑AS1 facilitates cell proliferation and invasion via regulating miR‑491‑5p/S100A11 axis in colorectal cancer.Int J Mol Med. 2021 Jul;48(1):138. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4971. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Int J Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34080639 Free PMC article.
-
Acrylamide-targeting renal miR-21a-5p/Fibrotic and miR122-5p/ inflammatory signaling pathways and the role of a green approach for nano-zinc detected via in silico and in vivo approaches.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 17;15:1413844. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1413844. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39086388 Free PMC article.
-
An Update of Long-Noncoding RNAs in Acute Kidney Injury.Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 8;13:849403. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.849403. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35350698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and validation of a genomic nomogram based on a ceRNA network for comprehensive analysis of obstructive sleep apnea.Front Genet. 2023 Mar 10;14:1084552. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1084552. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36968605 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of common molecular signatures of SARS-CoV-2 infection and its influence on acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 21;14:961642. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.961642. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37026010 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
