Influence of extension stem length and diameter on clinical and radiographic outcomes of revision total knee arthroplasty
- PMID: 31914984
- PMCID: PMC6950863
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-019-3030-1
Influence of extension stem length and diameter on clinical and radiographic outcomes of revision total knee arthroplasty
Abstract
Background: Extension stems provide stability to revision total knee arthroplasty (RTKA). Little is known regarding the relationship between stem characteristics and RTKA stability. We aimed to identify the relationship between canal filling ratio (CFR) and aseptic loosening following RTKA.
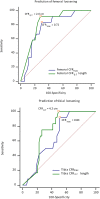
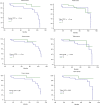
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed demographics, radiographic parameters, and outcomes associated with RTKA performed between 2008 and 2013 in a tertiary hospital. The inclusion criteria were: revision for aseptic loosening, hybrid fixation, minor bone defect, Zimmer® LCCK prosthesis, and follow-up > 24 months. Using the modified Knee Society radiographic scoring system, radiographic prosthesis loosening was defined as a radiolucent line (RLL) score ≥ 9 on the femoral side or ≥ 10 on the tibial side. We utilized receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis to evaluate the cutoff value for stem length and diameter in terms of prosthesis loosening or not. Furthermore, CFR-related parameters were analyzed with logistic regression to clarify their relationships with prosthesis loosening.
Results: Prosthesis loosening was detected in 17 of 65 patients included. On logistic regression analysis, male sex and severity of the tibial bone defect were associated with loosening. On multivariate analysis, male sex and bone defect severity were associated with loosening on the femoral side, while malalignment was associated with loosening on the tibial side. Protective factors included femoral CFR > 0.85, CFR > 0.7 for > 2 cm, and CFR > 0.7 for > 4 cm, as well as tibial CFR > 0.85.
Conclusions: To minimize loosening post-RTKA, femoral CFR > 0.7 for > 2 cm and tibial CFR > 0.85 are recommended. Risk factors may include male sex, bone defect severity, and malalignment.
Keywords: Aseptic loosening; Canal filling ratio; Extension stem; Revision total knee arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
High Rates of Early Septic Failure, but Low Rates of Aseptic Loosening After Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty With Contemporary Rotating-Hinge Prostheses.J Arthroplasty. 2025 Feb;40(2):460-466.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2024.08.013. Epub 2024 Aug 13. J Arthroplasty. 2025. PMID: 39147074
-
Varus-valgus constraint in 416 revision total knee arthroplasties with cemented stems provides a reliable reconstruction with a low subsequent revision rate at early to mid-term review.Bone Joint J. 2020 Apr;102-B(4):458-462. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.102B4.BJJ-2019-0719.R2. Bone Joint J. 2020. PMID: 32228079
-
Is hybrid fixation in revision TKA using LCCK prostheses reliable?Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2023 Sep;109(5):103583. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2023.103583. Epub 2023 Mar 4. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 36878283
-
Minimum 5-Year Clinical Outcomes and Survivorship for a Single Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty System Using Hybrid Fixation and Press-Fit Stems.J Arthroplasty. 2023 Jun;38(6S):S297-S301. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2023.03.083. Epub 2023 Mar 31. J Arthroplasty. 2023. PMID: 37003457 Review.
-
The Use of Metaphyseal Cones and Sleeves in Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2021 Sep 15;29(18):e904-e920. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-20-01431. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2021. PMID: 34432730 Review.
Cited by
-
Etiology of Total Knee Arthroplasty Revisions: A Two-Decade Institutional Perspective.Cureus. 2024 Feb 29;16(2):e55263. doi: 10.7759/cureus.55263. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38425332 Free PMC article.
-
Global mapping of institutional and hospital-based (Level II-IV) arthroplasty registries: a scoping review.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2024 Feb;34(2):1219-1251. doi: 10.1007/s00590-023-03691-y. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2024. PMID: 37768398 Free PMC article.
-
Isolated aseptic loosening in total knee arthroplasty: a comprehensive 10-year review of partial vs. total component revisions.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Oct 12;25(1):806. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07925-w. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39395955 Free PMC article.
-
Does medullary diameter to stem width ratio and stem length affect outcomes of revision total knee arthroplasties? A case series.Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2024 Jan 1;35(1):244-248. doi: 10.52312/jdrs.2023.1108. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2024. PMID: 38108187 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Surgeon Volume on Mechanical Complications after Resection Arthroplasty with Articulating Spacer.J Pers Med. 2024 May 3;14(5):490. doi: 10.3390/jpm14050490. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38793072 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

