Seven-day vonoprazan and low-dose amoxicillin dual therapy as first-line Helicobacter pylori treatment: a multicentre randomised trial in Japan
- PMID: 31915235
- PMCID: PMC7282559
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319954
Seven-day vonoprazan and low-dose amoxicillin dual therapy as first-line Helicobacter pylori treatment: a multicentre randomised trial in Japan
Abstract
Objective: To date, no randomised trials have compared the efficacy of vonoprazan and amoxicillin dual therapy with other standard regimens for Helicobacter pylori treatment. This study aimed to investigate the efficacy of the 7-day vonoprazan and low-dose amoxicillin dual therapy as a first-line H. pylori treatment, and compared this with vonoprazan-based triple therapy.
Design: This prospective, randomised clinical trial was performed at seven Japanese institutions. Patients with H. pylori-positive culture test and naive to treatment were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to either VA-dual therapy (vonoprazan 20 mg+amoxicillin 750 mg twice/day) or VAC-triple therapy (vonoprazan 20 mg+amoxicillin 750 mg+clarithromycin 200 mg twice/day) for 7 days, with stratification by age, sex, H. pylori antimicrobial resistance and institution. Eradication success was evaluated by 13C-urea breath test at least 4 weeks after treatment.
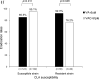
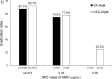
Results: Between October 2018 and June 2019, 629 subjects were screened and 335 were randomised. The eradication rates of VA-dual and VAC-triple therapies were 84.5% and 89.2% (p=0.203) by intention-to-treat analysis, respectively, and 87.1% and 90.2% (p=0.372) by per-protocol analysis, respectively. VA-dual was non-inferior to VAC-triple in the per-protocol analysis. The eradication rates in strains resistant to clarithromycin for VA-dual were significantly higher than those for VAC-triple (92.3% vs 76.2%; p=0.048). The incidence of adverse events was equal between groups.
Conclusion: The 7-day vonoprazan and low-dose amoxicillin dual therapy provided acceptable H. pylori eradication rates and a similar effect to vonoprazan-based triple therapy in regions with high clarithromycin resistance.
Trial registration number: UMIN000034140.
Keywords: antibiotics - clinical trials; clinical trials; gastric inflammation; helicobacter pylori - treatment.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: TG received honorarium from Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, the manufacturer of study drugs.
Figures

Comment in
-
Influence of clarithromycin on the bactericidal effect of amoxicillin in patients infected with clarithromycin-resistant strains of H. pylori.Gut. 2020 Nov;69(11):2056. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-320705. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Gut. 2020. PMID: 32051206 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
