Facial Clinimetric Evaluation Scale and Synkinesis Assessment Questionnaire Translation into Brazilian Portuguese: A Validation Study
- PMID: 31915465
- PMCID: PMC6946611
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0039-1697992
Facial Clinimetric Evaluation Scale and Synkinesis Assessment Questionnaire Translation into Brazilian Portuguese: A Validation Study
Abstract
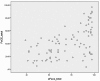
Introduction Facial nerve palsy results in both functional disability and psychological morbidity. There are several well-established grading scales to quantify the quality of life of these patients. Objective Translate and validate the Facial Clinimetric Evaluation (FaCE) scale and Synkinesis Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) to Brazilian Portuguese. Methods This study adopted a forward-backward translation method and performed cross-cultural adaptation. A pilot study was conducted to correct any confusing language and to evaluate content validity. A validation study was then performed. Internal consistency of the Brazilian Portuguese version of the FaCE and SAQ items was evaluated by Cronbach's alpha coefficient. Construct validity was assessed by Spearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient between FaCE and SAQ scores to eFACE, House-Brackmann, Short Form 12 (SF-12) and Facial Disability Index (FDI) (sub)scores. Results A total of 90 patients were included. Cronbach's alpha for total domain scored 0.881 for FaCE and 0.809 for SAQ. FaCE total score correlation to eFACE total and House-Brackmann showed Spearman's r value of 0.537 and -0.538, respectively ( p < 0.001). SAQ correlation to eFACE synkinesis subdomain was -0.449 ( p < 0.001). No correlation was found between SAQ and HB score. FaCE total score correlations were of 0.301 and 0.547 for SF-12 PCS and MCS, respectively ( p < 0.001). Correlation between FaCE total and FDI Physical and Social/well-being functions were 0.498 and 0.567 ( p < 0.001). Conclusion Brazilian Portuguese FaCE scale and SAQ versions achieved high validity and reliability in the present study. These translated instruments demonstrated good psychometric properties, being proper to use in clinical practice in Brazil and with Brazilian Portuguese speakers.
Keywords: facial palsy; quality of life; questionnaire; synkinesis; translation; validation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors have none to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Ishii L E, Godoy A, Encarnacion C O, Byrne P J, Boahene K D, Ishii M. What faces reveal: impaired affect display in facial paralysis. Laryngoscope. 2011;121(06):1138–1143. - PubMed
-
- Macgregor F C. Facial disfigurement: problems and management of social interaction and implications for mental health. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 1990;14(04):249–257. - PubMed
-
- Korb S, Wood A, Banks C A, Agoulnik D, Hadlock T A, Niedenthal P M. Asymmetry of Facial Mimicry and Emotion Perception in Patients With Unilateral Facial Paralysis. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2016;18(03):222–227. - PubMed
-
- House J W, Brackmann D E. Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1985;93(02):146–147. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

