What is the best treatment option for cervical spinal cord injury by os odontoideum in a patient with athetoid dystonic cerebral palsy?
- PMID: 31916917
- PMCID: PMC8725757
- DOI: 10.1080/10790268.2019.1706289
What is the best treatment option for cervical spinal cord injury by os odontoideum in a patient with athetoid dystonic cerebral palsy?
Abstract
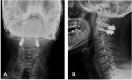
Context: Atlantoaxial instability in an athetoid dystonic cerebral palsy patient due to os odentoideum represents a rare cause of high-level cervical spinal cord injury. There is no evidence-based treatment protocol for this injury and a number of reports have debated whether nonsurgical or surgical treatment is the best option.Findings: Here, we report the case of a 32-year-old athetoid dystonic cerebral palsy patient with os odontoideum (OO) causing compressive myelopathy on the C1-2 levels. About two weeks after atlantoaxial fusion, the patient started an intensive rehabilitation program and maintained it for four weeks. He showed neurological and functional improvement at discharge after four weeks of training. There were further improvements in function and symptoms four weeks after discharge.Conclusion: Intensive rehabilitation programs are important for the recovery and good prognosis in spinal cord injury patients. However, rehabilitation of CP patients with spinal cord injury is often neglected. We provided intensive rehabilitation therapy to a patient for a cervical spinal cord injury by OO with athetoid dystonic cerebral palsy and achieved neurological and functional recovery.
Keywords: Athetoid dystonic cerebral palsy; Os odontoideum; Rehabilitation; Spinal cord injury.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Os odontoideum and craniovertebral junction instability secondary to dystonia: case series and review of the literature.Eur Spine J. 2024 Mar;33(3):1164-1170. doi: 10.1007/s00586-023-08044-1. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Eur Spine J. 2024. PMID: 37994987 Review.
-
Os Odontoideum in Children: Treatment Outcomes and Neurological Risk Factors.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019 Oct 2;101(19):1750-1760. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.19.00314. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019. PMID: 31577680
-
Acute Traumatic Cervical Cord Injury in Pediatric Patients with os Odontoideum: A Series of 6 Patients.World Neurosurg. 2015 Jun;83(6):1180.e1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2014.12.036. Epub 2014 Dec 19. World Neurosurg. 2015. PMID: 25535071
-
Os odontoideum as a rare but possible complication in children with dyskinetic cerebral palsy: a clinical and neuroradiologic study.J Child Neurol. 2011 Aug;26(8):1021-5. doi: 10.1177/0883073810397835. Epub 2011 May 26. J Child Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21616925
-
[Combined anterior-posterior arthrodesis en patient with athetoid cerebral palsy who developed spondylotic cervical mielopathy. Case report and review of literature].Neurocirugia (Astur). 2011 Jun;22(3):245-50. Neurocirugia (Astur). 2011. PMID: 21743945 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Os odontoideum and craniovertebral junction instability secondary to dystonia: case series and review of the literature.Eur Spine J. 2024 Mar;33(3):1164-1170. doi: 10.1007/s00586-023-08044-1. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Eur Spine J. 2024. PMID: 37994987 Review.
-
Reoperation Rates According to Surgical Approach After Operation for Degenerative Cervical Pathology in Patients With Athetoid Cerebral Palsy: A Nationwide Cohort Study.Global Spine J. 2025 Jan;15(1):21-30. doi: 10.1177/21925682241247486. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Global Spine J. 2025. PMID: 38631333 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
