Type I interferon response drives neuroinflammation and synapse loss in Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 31917687
- PMCID: PMC7108898
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI133737
Type I interferon response drives neuroinflammation and synapse loss in Alzheimer disease
Abstract
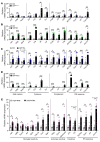
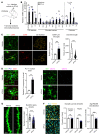
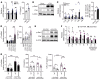
Type I interferon (IFN) is a key cytokine that curbs viral infection and cell malignancy. Previously, we demonstrated a potent IFN immunogenicity of nucleic acid-containing (NA-containing) amyloid fibrils in the periphery. Here, we investigated whether IFN is associated with β-amyloidosis inside the brain and contributes to neuropathology. An IFN-stimulated gene (ISG) signature was detected in the brains of multiple murine Alzheimer disease (AD) models, a phenomenon also observed in WT mouse brain challenged with generic NA-containing amyloid fibrils. In vitro, microglia innately responded to NA-containing amyloid fibrils. In AD models, activated ISG-expressing microglia exclusively surrounded NA+ amyloid β plaques, which accumulated in an age-dependent manner. Brain administration of rIFN-β resulted in microglial activation and complement C3-dependent synapse elimination in vivo. Conversely, selective IFN receptor blockade effectively diminished the ongoing microgliosis and synapse loss in AD models. Moreover, we detected activated ISG-expressing microglia enveloping NA-containing neuritic plaques in postmortem brains of patients with AD. Gene expression interrogation revealed that IFN pathway was grossly upregulated in clinical AD and significantly correlated with disease severity and complement activation. Therefore, IFN constitutes a pivotal element within the neuroinflammatory network of AD and critically contributes to neuropathogenic processes.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Immunology; Innate immunity; Neuroscience; Synapses.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Comment in
-
Intrinsic antiviral immunity drives neurodegeneration in Alzheimer disease.J Clin Invest. 2020 Apr 1;130(4):1622-1624. doi: 10.1172/JCI135906. J Clin Invest. 2020. PMID: 32149728 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Novel Role of COVID-19 in Alzheimer's Disease and Preventative Mitigation Strategies.J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;76(1):21-25. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200537. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020. PMID: 32538855 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG032051/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG043375/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG061566/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG054111/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054672/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG014449/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020670/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG017617/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS092615/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057587/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM088129/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG051812/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

