The dichotomous role of epiregulin in pain
- PMID: 31917773
- PMCID: PMC7166142
- DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001792
The dichotomous role of epiregulin in pain
Abstract
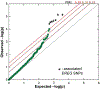
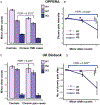
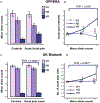
It has recently been shown that epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) contributes to the pathogenesis of pain. We scanned genetic markers within genes coding for receptors of the EGFR family (EGFR, ERBB2, ERBB3, and ERBB4) and their ligands (AREG, BTC, EGF, EPGN, EREG, HBEGF, MUC4, NRG1, NRG2, NRG3, NRG4, and TGFA) for association with self-reported pain intensity in patients with chronic facial pain who participated in the Orofacial Pain: Prospective Evaluation and Risk Assessment (OPPERA) cohort. We found that only epiregulin (EREG) was associated with pain. The strongest effect was observed for a minor allele at rs6836436 in EREG, which was associated with lower chronic pain intensity. However, the same allele was associated with higher facial pain intensity among cases with recent onset of facial pain. Similar trends were observed in an independent cohort of UK Biobank (UKB) where the minor allele at rs6836436 was associated with a higher number of acute pain sites but a lower number of chronic pain sites. Expression quantitative trait loci analyses established rs6836436 as a loss-of-function variant of EREG. Finally, we investigated the functional role of EREG using mouse models of chronic and acute pain. Injecting mice with an EREG monoclonal antibody reversed established mechanosensitivity in the complete Freund's adjuvant and spared nerve injury models of chronic pain. However, the EREG monoclonal antibody prolonged allodynia when administered during the development of complete Freund's adjuvant-induced mechanosensitivity and enhanced pain behavior in the capsaicin model of acute pain.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statements
The authors have no conflicts of interest related to this study to declare.
Figures


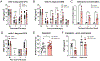
References
-
- Aaron LA, Burke MM, Buchwald D. Overlapping conditions among patients with chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia, and temporomandibular disorder. Archives of Internal Medicine 2000;160(2):221–227. - PubMed
-
- Bair E, Brownstein NC, Ohrbach R, Greenspan JD, Dubner R, Fillingim RB, Maixner W, Smith SB, Diatchenko L, Gonzalez Y, Gordon SM, Lim PF, Ribeiro-Dasilva M, Dampier D, Knott C, Slade GD. Study protocol, sample characteristics, and loss to follow-up: the OPPERA prospective cohort study. J Pain 2013;14(12 Suppl):T2–19. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barbero M, Fernandez-de-Las-Penas C, Palacios-Cena M, Cescon C, Falla D. Pain extent is associated with pain intensity but not with widespread pressure or thermal pain sensitivity in women with fibromyalgia syndrome. Clin Rheumatol 2017;36(6):1427–1432. - PubMed
-
- Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005;21(2):263–265. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate - a Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B-Stat Methodol 1995;57(1):289–300.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

