The microenvironmental and metabolic aspects of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 31918403
- PMCID: PMC7000339
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.102610
The microenvironmental and metabolic aspects of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
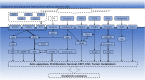
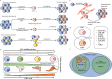
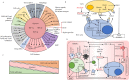
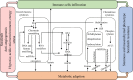
In most cases, sorafenib-resistant HCC cells exhibit significant mesenchymal phenotype and stemness features. In this context, tumor cells might undergo cell fate transition in response to sorafenib or other targeted drugs in the presence or absence of genetic mutations. Therefore, understanding the major characteristics of drug-resistant cells state helps to discover new treatments that overcome drug resistance. To note, little is known about the metabolic or microenvironmental aspects of the certain tumor cell states beyond the genome. This review mainly focuses on the underlying mechanisms of acquired sorafenib resistance based on CSCs and EMT models, which explain tumor heterogeneity and have been considered the major cause of secondary sorafenib resistance. In particular, it discusses how the tumor microenvironment and tumor metabolism regulate cell stemness, mesenchymal state, and sorafenib resistance through epigenetic regulations, and provides reliable targets that might have synergetic effect with sorafenib.
Keywords: Cancer stem cells; Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; Hypoxia; Sorafenib resistance; Tumor metabolism; Tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Overcoming sorafenib treatment-resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: A future perspective at a time of rapidly changing treatment paradigms.EBioMedicine. 2020 Feb;52:102644. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102644. Epub 2020 Jan 31. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 32014823 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Torre L.A., Bray F., Siegel R.L., Ferlay J., Lortet‐Tieulent J., Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Cheng A.-L., Kang Y.-K., Chen Z. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:25–34. - PubMed
-
- Llovet J.M., Ricci S., Mazzaferro V. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378–390. - PubMed
-
- Xiang D.-M., Sun W., Zhou T. Oncofetal HLF transactivates c-Jun to promote hepatocellular carcinoma development and sorafenib resistance. Gut. 2019;68:1858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

