Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate β cell dysfunction of human type 2 diabetic islets by reversing β cell dedifferentiation
- PMID: 31918404
- PMCID: PMC7000334
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.102615
Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate β cell dysfunction of human type 2 diabetic islets by reversing β cell dedifferentiation
Abstract
Background: A physiological hallmark of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is β cell dysfunction. Despite adequate treatment, it is an irreversible process that follows disease progression. Therefore, the development of novel therapies that restore β cell function is of utmost importance.
Methods: This study aims to unveil the mechanistic action of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) by investigating its impact on isolated human T2DM islets ex vivo and in vivo.
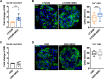
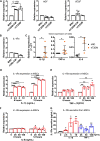
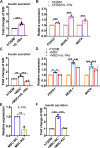
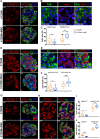
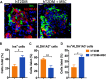
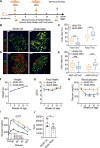
Findings: We propose that MSCs can attenuate β cell dysfunction by reversing β cell dedifferentiation in an IL-1Ra-mediated manner. In response to the elevated expression of proinflammatory cytokines in human T2DM islet cells, we observed that MSCs was activated to secret IL-1R antagonist (IL-1Ra) which acted on the inflammed islets and reversed β cell dedifferentiation, suggesting a crosstalk between MSCs and human T2DM islets. The co-transplantation of MSCs with human T2DM islets in diabetic SCID mice and intravenous infusion of MSCs in db/db mice revealed the reversal of β cell dedifferentiation and improved glycaemic control in the latter.
Interpretation: This evidence highlights the potential of MSCs in future cell-based therapies regarding the amelioration of β cell dysfunction.
Keywords: Inflammation; Mesenchymal stem cells; Type 2 diabetes mellitus; β cell dedifferentiation; β cell dysfunction.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest No conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reversion of early- and late-stage β-cell dedifferentiation by human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in type 2 diabetic mice.Cytotherapy. 2021 Jun;23(6):510-520. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2021.01.005. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Cytotherapy. 2021. PMID: 33736932
-
Amyloid formation disrupts the balance between interleukin-1β and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in human islets.Mol Metab. 2017 May 31;6(8):833-844. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.05.016. eCollection 2017 Aug. Mol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28752047 Free PMC article.
-
Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells direct macrophage polarization to alleviate pancreatic islets dysfunction in type 2 diabetic mice.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jul 9;9(7):760. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0801-9. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29988034 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) and IL-1Ra producing mesenchymal stem cells as modulators of diabetogenesis.Autoimmunity. 2010 Jun;43(4):255-63. doi: 10.3109/08916930903305641. Autoimmunity. 2010. PMID: 19845478 Review.
-
Applicability of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Aug 28;10(1):274. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1362-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31455405 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regeneration of β cells from cell phenotype conversion among the pancreatic endocrine cells.Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2022 Mar 2;8(1):1-4. doi: 10.1002/cdt3.15. eCollection 2022 Mar. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35620156 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells from Type 2 Diabetics Reveal Conservative Alterations in Multidimensional Characteristics.Int J Stem Cells. 2020 Jul 30;13(2):268-278. doi: 10.15283/ijsc20028. Int J Stem Cells. 2020. PMID: 32587133 Free PMC article.
-
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Facilitates Shift of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Ex Vivo Differentiation toward Osteogenesis among Patients with Obesity.Life (Basel). 2022 May 6;12(5):688. doi: 10.3390/life12050688. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35629356 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells: ideal seeds for treating diseases.Hum Cell. 2021 Nov;34(6):1585-1600. doi: 10.1007/s13577-021-00578-0. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Hum Cell. 2021. PMID: 34272720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers of aging.Sci China Life Sci. 2023 May;66(5):893-1066. doi: 10.1007/s11427-023-2305-0. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Sci China Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37076725 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- IDF . 8th edn. International Diabetes Federation; Brussels, Belgium: 2017. IDF Diabetes Atlas.http://www.diabetesatlas.org2017
-
- Taniguchi A., Fukushima M., Sakai M., Nagata I., Doi K., Nagasaka S. Insulin secretion, insulin sensitivity, and glucose effectiveness in nonobese individuals with varying degrees of glucose tolerance. Diabetes care. 2000;23(1):127–128. - PubMed
-
- Donath M.Y., Shoelson S.E. Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11(2):98–107. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

