Therapeutic Approaches to Gastric Hepatoid Adenocarcinoma: Current Perspectives
- PMID: 31920320
- PMCID: PMC6934111
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S204303
Therapeutic Approaches to Gastric Hepatoid Adenocarcinoma: Current Perspectives
Abstract
Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the stomach (HAS) is a rare subgroup of gastric cancer (GC). Morphologically, this tumor exhibits both adenocarcinomatous and hepatocellular differentiation, and most tumors show immunohistochemical staining for alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) or elevated AFP serum levels. The diagnosis of HAS is frequently delayed, and at least half of patients have advanced disease at the time of diagnosis. Despite a lack of evidence, treatment approaches have mostly followed principles for the treatment of common gastric cancer (CGC), including radical surgery in eligible patients with curative intent. The indications for and the type of adjuvant systemic treatments remain unclear. Additionally, there is a lack of evidence allowing any firm conclusions to be drawn regarding the best treatment for patients with metastatic HAS (mHAS). Chemotherapy regimens, including cisplatin-based chemotherapy, are considered the most efficient first-line systemic treatment in advanced situations. Their combination with targeted therapy (i.e., trastuzumab) in HER2-positive tumors seems promising. The rarity of these patients and the scarce and heterogeneous literature on this particular subgroup of GC make it difficult to provide any robust evidence for the clinical management of patients with HAS.
Keywords: alpha-fetoprotein; gastric; hepatoid adenocarcinoma; prognosis; stomach; therapy.
© 2019 Søreide.
Conflict of interest statement
Professor Jon Arne Søreide, MD, PhD, FACS, FISS is an approved specialist in general- and gastrointestinal surgery. The author reports no conflicts of interest in this work.
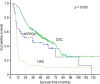
Figures
References
-
- Bourreille J, Metayer P, Sauger F, Fondimare A. Existence d`alpha fetoprotein au cours d`un cancer secondaire du foie d`origine gastrique. Press Med. 1970;78(28):1277–1278. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

