Hyperuricemia and Hypertension: Links and Risks
- PMID: 31920373
- PMCID: PMC6935283
- DOI: 10.2147/IBPC.S184685
Hyperuricemia and Hypertension: Links and Risks
Abstract
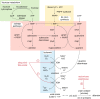
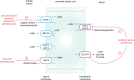
Hyperuricemia has long been recognized to be associated with increased cardiovascular risk, including risk of developing hypertension. Epidemiological findings suggest that the link with hypertension is stronger in children and adolescents. Uric acid acts as a strong antioxidant compound in the extracellular environment but has pro-inflammatory effects within the intracellular setting. A chronic phase of microvascular injury is known to occur after prolonged periods of hyperuricemia. This is proposed to contribute to afferent arteriolopathy and elevation of blood pressure that may become unresponsive to uric acid-lowering therapies over time. Studies have struggled to infer direct causality of hyperuricemia due to a vast number of confounders including body mass index. The aim of this review is to present the available data and highlight the need for large scale prospective randomized controlled trials in this area. At present, there is limited evidence to support a role for uric acid-lowering therapies in helping mitigate the risk of hypertension.
Keywords: cardiovascular; chronic kidney disease; hypertension; hyperuricemia; urate.
© 2019 Stewart et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Stevens G. Global health risks: mortality and burden of disease attributable to selected major risks. Bull World Health Organ. 2009.
-
- Mahomed FA. On chronic Bright’s disease, and its essential symptoms. Lancet. 1879;1:389–404.
-
- Roch-Ramel F, Guisan B. Renal transport of urate in humans. News Physiol Sci. 1999;Apr(14):80–84. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

