Baroreflex Sensitivity Predicts Response to Metoprolol in Children With Vasovagal Syncope: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 31920498
- PMCID: PMC6923178
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2019.01329
Baroreflex Sensitivity Predicts Response to Metoprolol in Children With Vasovagal Syncope: A Pilot Study
Abstract
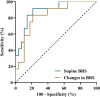
Objective: To explore the role of baroreflex sensitivity (BRS) in the head-up tilt test (HUTT) in predicting the therapeutic response of vasovagal syncope (VVS) patients to metoprolol. Materials and Methods: Vasovagal syncope patients treated with metoprolol were enrolled in this study and were classified as responders or non-responders according to changes in their symptom scores before and after metoprolol treatment. Values of BRS in the supine position and at positive response occurrence in the HUTT were obtained, and BRS changes from supine to positive response occurrence were calculated. Differences between responders and non-responders were analyzed. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was performed to assess the value of BRS for predicting the therapeutic efficacy of metoprolol in pediatric patients with VVS. Results: Forty patients (14 boys; 11.8 ± 2.5 years) diagnosed with VVS were recruited in the study, 28 of whom were verified to be responders to metoprolol and 12 of whom were verified as non-responders. They did not show any differences in baseline characteristics and hemodynamics in the HUTT (p > 0.05). However, the responders had an obviously increased supine BRS value compared to the non-responders (16.9 ± 7.7 ms/mmHg vs. 7.6 ± 3.8 ms/mmHg; p < 0.01). No difference in BRS at positive response occurrence was observed between the two groups (8.9 ± 8.5 ms/mmHg vs. 10.6 ± 9.8 ms/mmHg; p > 0.05). Accordingly, the changes in the BRS of responders were more obvious than in non-responders (8.0 ± 7.8 ms/mmHg vs. -3.0 ± 10.4 ms/mmHg; p < 0.01). The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for the predictive value of supine BRS was 0.887 (95% CI, 0.779-0.995; p < 0.01). A cut-off value of 10 ms/mmHg yielded a sensitivity and specificity of 82 and 83%, respectively, in predicting the therapeutic efficacy of metoprolol in pediatric VVS patients. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for the predictive value of BRS changes was 0.827 (95% CI, 0.693-0.962; p < 0.01). A cut-off value of 4 ms/mmHg yielded a sensitivity and specificity of 71 and 83%, respectively. Conclusion: Baroreflex sensitivity may predict the response of children with VVS to metoprolol.
Keywords: baroreflex sensitivity; children; metoprolol; therapeutic response; vasovagal syncope.
Copyright © 2019 Tao, Li, Tang, Jin and Du.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multivariate predictive model of the therapeutic effects of metoprolol in paediatric vasovagal syncope: a multi-centre study.EBioMedicine. 2025 Mar;113:105595. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105595. Epub 2025 Feb 12. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 39946834 Free PMC article.
-
Baroreflex sensitivity predicts therapeutic effects of metoprolol on pediatric postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Sep 14;9:930994. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.930994. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36187012 Free PMC article.
-
Baroreflex Sensitivity Predicts the Head-Up Tilt Test Induced Asystole Among Patients With Suspected Vasovagal Syncope.Am J Cardiol. 2025 Aug 6;257:72-76. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2025.07.046. Online ahead of print. Am J Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40780451
-
A higher peak heart rate during head-up tilt test predicts the therapeutic efficacy of metoprolol in vasovagal syncope.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Oct 18;24(1):576. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04249-4. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39425043 Free PMC article.
-
Poincaré Plot Can Be a Useful Tool to Select Potential Responders to Metoprolol Therapy in Children with Vasovagal Syncope.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Mar 8;15:2681-2693. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S352928. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35300141 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Multivariate predictive model of the therapeutic effects of metoprolol in paediatric vasovagal syncope: a multi-centre study.EBioMedicine. 2025 Mar;113:105595. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105595. Epub 2025 Feb 12. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 39946834 Free PMC article.
-
Body mass index is a promising predictor of response to oral rehydration saline in children with vasovagal syncope.Chin Med J (Engl). 2020 Nov 2;134(4):463-468. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001168. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020. PMID: 33617185 Free PMC article.
-
The predictive value of urine specific gravity in the diagnosis of vasovagal syncope in children and adolescents.Ital J Pediatr. 2021 Apr 17;47(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s13052-021-01043-2. Ital J Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33865429 Free PMC article.
-
Age and mean platelet volume-based nomogram for predicting the therapeutic efficacy of metoprolol in Chinese pediatric patients with vasovagal syncope.World J Pediatr. 2024 Sep;20(9):957-965. doi: 10.1007/s12519-024-00802-5. Epub 2024 Apr 13. World J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38613734 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Efficacy of Empirical Therapy in Children with Vasovagal Syncope.Children (Basel). 2022 Jul 17;9(7):1065. doi: 10.3390/children9071065. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884049 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bari V., Vaini E., Pistuddi V., Fantinato A., Cairo B., De Maria B., et al. (2019). Comparison of causal and non-causal strategies for the assessment of baroreflex sensitivity in predicting acute kidney dysfunction after coronary artery bypass grafting. Front. Physiol. 10:1319. 10.3389/fphys.2019.01319 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bertinieri G., di Rienzo M., Cavallazzi A., Ferrari A. U., Pedotti A., Mancia G. (1985). A new approach to analysis of the arterial baroreflex. J. Hypertens. Suppl. 3 S79–S81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

