A Comparison of Neural Decoding Methods and Population Coding Across Thalamo-Cortical Head Direction Cells
- PMID: 31920565
- PMCID: PMC6914739
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2019.00075
A Comparison of Neural Decoding Methods and Population Coding Across Thalamo-Cortical Head Direction Cells
Abstract
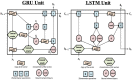
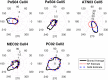
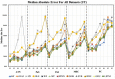
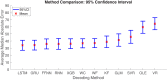
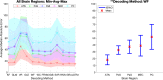
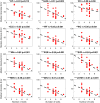
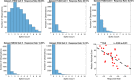
Head direction (HD) cells, which fire action potentials whenever an animal points its head in a particular direction, are thought to subserve the animal's sense of spatial orientation. HD cells are found prominently in several thalamo-cortical regions including anterior thalamic nuclei, postsubiculum, medial entorhinal cortex, parasubiculum, and the parietal cortex. While a number of methods in neural decoding have been developed to assess the dynamics of spatial signals within thalamo-cortical regions, studies conducting a quantitative comparison of machine learning and statistical model-based decoding methods on HD cell activity are currently lacking. Here, we compare statistical model-based and machine learning approaches by assessing decoding accuracy and evaluate variables that contribute to population coding across thalamo-cortical HD cells.
Keywords: anterior thalamus; memory; navigation; parahippocampal; parietal; spatial behavior.
Copyright © 2019 Xu, Wu, Winter, Mehlman, Butler, Simmons, Harvey, Berkowitz, Chen, Taube, Wilber and Clark.
Figures





References
-
- Berens P. (2009). CircStat: a MATLAB toolbox for circular statistics. J. Stat. Softw. 31 1–21.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

