Identifying Vulnerable Brain Networks in Mouse Models of Genetic Risk Factors for Late Onset Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 31920610
- PMCID: PMC6914731
- DOI: 10.3389/fninf.2019.00072
Identifying Vulnerable Brain Networks in Mouse Models of Genetic Risk Factors for Late Onset Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
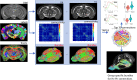
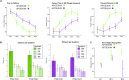
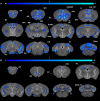
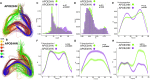
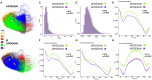
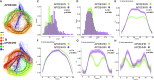
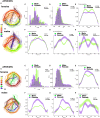
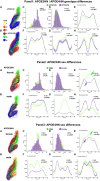
The major genetic risk for late onset Alzheimer's disease has been associated with the presence of APOE4 alleles. However, the impact of different APOE alleles on the brain aging trajectory, and how they interact with the brain local environment in a sex specific manner is not entirely clear. We sought to identify vulnerable brain circuits in novel mouse models with homozygous targeted replacement of the mouse ApoE gene with either human APOE3 or APOE4 gene alleles. These genes are expressed in mice that also model the human immune response to age and disease-associated challenges by expressing the human NOS2 gene in place of the mouse mNos2 gene. These mice had impaired learning and memory when assessed with the Morris water maze (MWM) and novel object recognition (NOR) tests. Ex vivo MRI-DTI analyses revealed global and local atrophy, and areas of reduced fractional anisotropy (FA). Using tensor network principal component analyses for structural connectomes, we inferred the pairwise connections which best separate APOE4 from APOE3 carriers. These involved primarily interhemispheric connections among regions of olfactory areas, the hippocampus, and the cerebellum. Our results also suggest that pairwise connections may be subdivided and clustered spatially to reveal local changes on a finer scale. These analyses revealed not just genotype, but also sex specific differences. Identifying vulnerable networks may provide targets for interventions, and a means to stratify patients.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; diffusion tensor (DT) MRI; magnetic resonance imaging; morphometric; mouse model; neurodegeneration; tract based analysis; tractography.
Copyright © 2019 Badea, Wu, Shuff, Wang, Anderson, Qi, Johnson, Wilson, Koudoro, Garyfallidis, Colton and Dunson.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Brain network fingerprints of Alzheimer's disease risk factors in mouse models with humanized APOE alleles.Magn Reson Imaging. 2024 Dec;114:110251. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2024.110251. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Magn Reson Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39362319
-
APOE, Immune Factors, Sex, and Diet Interact to Shape Brain Networks in Mouse Models of Aging.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 1:2023.10.04.560954. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.04.560954. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39005377 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Human apoE targeted replacement mouse lines: h-apoE4 and h-apoE3 mice differ on spatial memory performance and avoidance behavior.Behav Brain Res. 2005 Apr 15;159(1):1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2004.09.019. Epub 2004 Nov 6. Behav Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 15794991
-
The role of diffusion tensor imaging and fractional anisotropy in the evaluation of patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a literature review.Neurosurg Focus. 2016 Sep;41(3):E12. doi: 10.3171/2016.6.FOCUS16192. Neurosurg Focus. 2016. PMID: 27581308 Review.
-
APOE-related biomarker profiles in non-pathological aging and early phases of Alzheimer's disease.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2013 Sep;37(8):1322-35. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.05.006. Epub 2013 May 20. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2013. PMID: 23701948 Review.
Cited by
-
Feature attention graph neural network for estimating brain age and identifying important neural connections in mouse models of genetic risk for Alzheimer's disease.Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2024 Jul 31;2:imag-2-00245. doi: 10.1162/imag_a_00245. eCollection 2024. Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2024. PMID: 40800544 Free PMC article.
-
A time-course study of actively stained mouse brains: Diffusion tensor imaging parameters and connectomic stability over 1 year.NMR Biomed. 2022 Jan;35(1):e4611. doi: 10.1002/nbm.4611. Epub 2021 Sep 23. NMR Biomed. 2022. PMID: 34558744 Free PMC article.
-
Absolute Winding Number Differentiates Mouse Spatial Navigation Strategies With Genetic Risk for Alzheimer's Disease.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jun 17;16:848654. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.848654. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35784847 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein-E deficiency leads to brain network alteration characterized by diffusion MRI and graph theory.Front Neurosci. 2023 Nov 21;17:1183312. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1183312. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38075287 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep deprivation aggravated amyloid β oligomers-induced damage to the cerebellum of rats: Evidence from magnetic resonance imaging.Aging Brain. 2023 Aug 5;4:100091. doi: 10.1016/j.nbas.2023.100091. eCollection 2023. Aging Brain. 2023. PMID: 37600754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson R. J., Wang N., Cook J. J., Cofer G. P., Dibb R., Johnson G. A., et al. (2018b). A high performance computing cluster implementation of compressed sensing reconstruction for MR histology. Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 26.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

