Stereotactic Radiation Therapy (SRT) for Brain Metastases of Multiple Primary Tumors: A Single Institution Retrospective Analysis
- PMID: 31921625
- PMCID: PMC6914765
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01352
Stereotactic Radiation Therapy (SRT) for Brain Metastases of Multiple Primary Tumors: A Single Institution Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
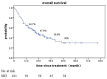
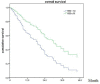
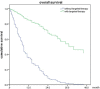
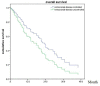
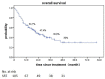
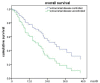
Purpose: To evaluate the efficiency and side effects of stereotactic radiation therapy (SRT) with or without other treatments for brain metastases (BM) from various primary tumors. Methods: This was a retrospective analysis of 161 patients with brain metastases treated with SRT. Clinical data, EGFR mutation status and survival data were collected. Follow-up data was analyzed until December 2018. Kaplan-Meier and Cox proportional hazards regression analyses were used for the survival analysis. Results: The median overall survival (OS) was 19 months. No difference was observed in OS between SRT group and SRT + whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) groups (p = 0.717). Statistically significant factors of better OS after univariable analysis were no extracranial metastases (p = 0.016), BED10-SRT≥50Gy (p = 0.049), oligometastases (1-3 brain metastases) (p < 0.001), GPA score≥2.5 (p = 0.003), RPA class I (p = 0.026), NSCLC tumor type (p = 0.006), targeted therapy (p < 0.001) and controlled extracranial disease (p = 0.011). Multivariate analysis indicated that higher BED10-SRT (≥50Gy, HR = 0.504, p = 0.027), controlled extracranial disease (HR = 0.658, p = 0.039) and targeted therapy (HR = 0.157, <0.001) were independent favorable predictors for OS. Besides that, we also find that the median overall survival (OS) was 22 months in NSCLC patients and controlled extracranial disease (HR = 0.512, p = 0.012) and targeted therapy (HR = 0.168, < 0.001) were independent favorable predictors for OS. Conclusion: For patients with brain metastases, stable extracranial disease, higher BED10-SRT (≥50Gy) and targeted therapy may predict a favorable prognosis.
Keywords: brain metastasis; non–small-cell lung cancer; overall survival; prognostic factors; stereotactic radiation therapy.
Copyright © 2019 Gu, Qing, Zhu, Ju, Cao, Jia, Shen, Cao, Fang and Zhang.
Figures

References
-
- Goncalves PH, Peterson SL, Vigneau FD, Shore RD, Quarshie WO, Islam K, et al. . Risk of brain metastases in patients with nonmetastatic lung cancer: Analysis of the Metropolitan Detroit Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) data. Cancer. (2016) 122:1921–7. 10.1002/cncr.30000 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

