Molecular Mechanism of the Antiproliferative Activity of Short Immunostimulating dsRNA
- PMID: 31921696
- PMCID: PMC6933605
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01454
Molecular Mechanism of the Antiproliferative Activity of Short Immunostimulating dsRNA
Abstract
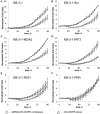
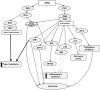
Small double-stranded RNAs with certain sequence motifs are able to interact with pattern-recognition receptors and activate the innate immune system. Recently, we identified a set of short double-stranded 19-bp RNA molecules with 3-nucleotide 3'-overhangs that exhibited pronounced antiproliferative activity against cancer cells in vitro, and antitumor and antimetastatic activities in mouse models in vivo. The main objectives of this study were to identify the pattern recognition receptors that mediate the antiproliferative action of immunostimulating RNA (isRNA). Two cell lines, epidermoid carcinoma KB-3-1 cells and lung cancer A549 cells, were used in the study. These lines respond to the action of isRNA by a decrease in the growth rate, and in the case of A549 cells, also by a secretion of IL-6. Two sets of cell lines with selectively silenced genes encoding potential sensors and signal transducers of isRNA action were obtained on the basis of KB-3-1 and A549 cells. It was found that the selective silencing of PKR and RIG-I genes blocked the antiproliferative effect of isRNA, both in KB-3-1 and A549 cells, whereas the expression of MDA5 and IRF3 was not required for the antiproliferative action of isRNA. It was shown that, along with PKR and RIG-I genes, the expression of IRF3 also plays a role in isRNA mediated IL-6 synthesis in A549 cells. Thus, PKR and RIG-I sensors play a major role in the anti-proliferative signaling triggered by isRNA.
Keywords: IL-6; PKR; RIG-I; antiproliferative activity; gene silencing; immunostimulating dsRNA; pattern recognition receptors; shRNA.
Copyright © 2019 Zharkov, Zenkova, Vlassov and Chernolovskaya.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Impact of Chemical Modifications on the Interferon-Inducing and Antiproliferative Activity of Short Double-Stranded Immunostimulating RNA.Molecules. 2024 Jul 7;29(13):3225. doi: 10.3390/molecules29133225. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38999177 Free PMC article.
-
Short double-stranded RNA with immunostimulatory activity: sequence dependence.Nucleic Acid Ther. 2012 Jun;22(3):196-204. doi: 10.1089/nat.2011.0328. Epub 2012 Apr 17. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2012. PMID: 22509928
-
Double-stranded RNA induces an antiviral defense status in epidermal keratinocytes through TLR3-, PKR-, and MDA5/RIG-I-mediated differential signaling.J Immunol. 2008 Aug 15;181(4):2694-704. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.4.2694. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18684960
-
Structural basis of innate immune recognition of viral RNA.Cell Microbiol. 2013 Mar;15(3):386-94. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12061. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Cell Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23110455 Review.
-
siRNA and isRNA: two edges of one sword.Mol Ther. 2006 Oct;14(4):463-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2006.06.001. Epub 2006 Jul 31. Mol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16877044 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of the Composition of Cationic Liposomes on the Performance of Cargo Immunostimulatory RNA.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 23;15(9):2184. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092184. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765155 Free PMC article.
-
Immunostimulating RNA Delivered by P1500 PEGylated Cationic Liposomes Limits Influenza Infection in C57Bl/6 Mice.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Sep 14;12(9):875. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12090875. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32937880 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Innate Immunity by Therapeutic Nucleic Acids.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 12;22(24):13360. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413360. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948156 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

