Nanomedicine Approaches for the Pulmonary Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis
- PMID: 31921811
- PMCID: PMC6927921
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00406
Nanomedicine Approaches for the Pulmonary Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis
Abstract
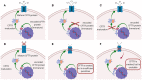
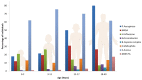
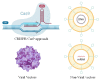
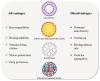
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disease affecting today nearly 70,000 patients worldwide and characterized by a hypersecretion of thick mucus difficult to clear arising from the defective CFTR protein. The over-production of the mucus secreted in the lungs, along with its altered composition and consistency, results in airway obstruction that makes the lungs susceptible to recurrent and persistent bacterial infections and endobronchial chronic inflammation, which are considered the primary cause of bronchiectasis, respiratory failure, and consequent death of patients. Despite the difficulty of treating the continuous infections caused by pathogens in CF patients, various strategies focused on the symptomatic therapy have been developed during the last few decades, showing significant positive impact on prognosis. Moreover, nowadays, the discovery of CFTR modulators as well as the development of gene therapy have provided new opportunity to treat CF. However, the lack of effective methods for delivery and especially targeted delivery of therapeutics specifically to lung tissues and cells limits the efficiency of the treatments. Nanomedicine represents an extraordinary opportunity for the improvement of current therapies and for the development of innovative treatment options for CF previously considered hard or impossible to treat. Due to the peculiar environment in which the therapies have to operate characterized by several biological barriers (pulmonary tract, mucus, epithelia, bacterial biofilm) the use of nanotechnologies to improve and enhance drug delivery or gene therapies is an extremely promising way to be pursued. The aim of this review is to revise the currently used treatments and to outline the most recent progresses about the use of nanotechnology for the management of CF.
Keywords: cystic fibrosis; drug delivery; gene therapy; lung pathology; nanoparticles.
Copyright © 2019 Velino, Carella, Adamiano, Sanguinetti, Vitali, Catalucci, Bugli and Iafisco.
Figures
References
-
- Alikhani Z., Salouti M., Ardestani M. S. (2018). Synthesis and immunological evaluation of a nanovaccine based on PLGA nanoparticles and alginate antigen against infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 4, 1–9. 10.1088/2057-1976/aabfac - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

