Cytotoxicity-Related Bioeffects Induced by Nanoparticles: The Role of Surface Chemistry
- PMID: 31921818
- PMCID: PMC6920110
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00414
Cytotoxicity-Related Bioeffects Induced by Nanoparticles: The Role of Surface Chemistry
Abstract
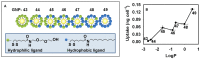
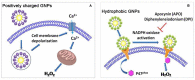
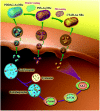
Nanoparticles (NPs) are widely used in a variety of fields, including those related to consumer products, architecture, energy, and biomedicine. Once they enter the human body, NPs contact proteins in the blood and interact with cells in organs, which may induce cytotoxicity. Among the various factors of NP surface chemistry, surface charges, hydrophobicity levels and combinatorial decorations are found to play key roles inregulating typical cytotoxicity-related bioeffects, including protein binding, cellular uptake, oxidative stress, autophagy, inflammation, and apoptosis. In this review, we summarize the recent progress made in directing the levels and molecular pathways of these cytotoxicity-related effects by the purposeful design of NP surface charge, hydrophobicity, and combinatorial decorations.
Keywords: PEG; charge; cytotoxicity; hydrophobicity; nanoparticles; surface chemistry.
Copyright © 2019 Sun, Jiang, Wu, Bai and Zhai.
Figures
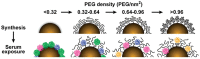




References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

