Modeling cell-cell communication for immune systems across space and time
- PMID: 31922054
- PMCID: PMC6941841
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coisb.2019.10.008
Modeling cell-cell communication for immune systems across space and time
Abstract
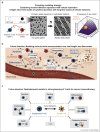
Communicating is crucial for cells to coordinate their behaviors. Immunological processes, involving diverse cytokines and cell types, are ideal for developing frameworks for modeling coordinated behaviors of cells. Here, we review recent studies that combine modeling and experiments to reveal how immune systems use autocrine, paracrine, and juxtacrine signals to achieve behaviors such as controlling population densities and hair regenerations. We explain that models are useful because one can computationally vary numerous parameters, in experimentally infeasible ways, to evaluate alternate immunological responses. For each model, we focus on the length-scales and time-scales involved and explain why integrating multiple length-scales and time-scales in a model remain challenging. We suggest promising modeling strategies for meeting this challenge and their practical consequences.
Keywords: Cellular automata; Cellular communication; Cytokines; Design principles; Immune systems; Modeling; Multicellular systems; Reaction–diffusion equations.
© 2019 The Authors.
Figures


References
-
- Francis K., Palsson B.O. Effective intercellular communication distances are determined by the relative time constants for cyto/chemokine secretion and diffusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1997;94:12258–12262. - PMC - PubMed
-
This study mathematically shows how a single cell secreting cytokines or chemokines could achieve various length-scales and time-scales of communication based on physical and chemical parameters.
-
- Shvartsman S.Y., Steven Wiley H., Deen W.M., Lauffenburger D.A. Spatial range of autocrine signaling: modeling and computational analysis. Biophys J. 2001;81:1854–1867. - PMC - PubMed
-
This study combines Brownian motion theory, Monte Carlo simulations and reaction-diffusion models to show how the spatial range of cell-secreted autocrine signals can be tuned based on molecular and cellular parameters.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
