Metabolic signature in nucleus accumbens for anti-depressant-like effects of acetyl-L-carnitine
- PMID: 31922486
- PMCID: PMC6970538
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.50631
Metabolic signature in nucleus accumbens for anti-depressant-like effects of acetyl-L-carnitine
Abstract
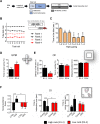
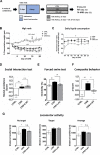
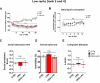
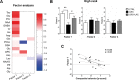
Emerging evidence suggests that hierarchical status provides vulnerability to develop stress-induced depression. Energy metabolic changes in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) were recently related to hierarchical status and vulnerability to develop depression-like behavior. Acetyl-L-carnitine (LAC), a mitochondria-boosting supplement, has shown promising antidepressant-like effects opening therapeutic opportunities for restoring energy balance in depressed patients. We investigated the metabolic impact in the NAc of antidepressant LAC treatment in chronically-stressed mice using 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS). High rank, but not low rank, mice, as assessed with the tube test, showed behavioral vulnerability to stress, supporting a higher susceptibility of high social rank mice to develop depressive-like behaviors. High rank mice also showed reduced levels of several energy-related metabolites in the NAc that were counteracted by LAC treatment. Therefore, we reveal a metabolic signature in the NAc for antidepressant-like effects of LAC in vulnerable mice characterized by restoration of stress-induced neuroenergetics alterations and lipid function.
Keywords: 1H-MRS; acetyl-L-carnitine; brain metabolism; depression; mouse; neuroscience; nucleus accumbens; stress.
© 2020, Cherix et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AC, TL, JG, JR, BM, CN, RG, CS No competing interests declared
Figures





References
-
- Aureli T, Miccheli A, Ricciolini R, Di Cocco ME, Ramacci MT, Angelucci L, Ghirardi O, Conti F. Aging brain: effect of acetyl-L-carnitine treatment on rat brain energy and phospholipid metabolism. A study by 31P and 1H NMR spectroscopy. Brain Research. 1990;526:108–112. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90255-A. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aureli T, Miccheli A, Di Cocco ME, Ghirardi O, Giuliani A, Ramacci MT, Conti F. Effect of acetyl-L-carnitine on recovery of brain phosphorus metabolites and lactic acid level during reperfusion after cerebral ischemia in the rat--study by 13P- and 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Brain Research. 1994;643:92–99. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)90013-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

