Structural basis for COMPASS recognition of an H2B-ubiquitinated nucleosome
- PMID: 31922488
- PMCID: PMC7039682
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.53199
Structural basis for COMPASS recognition of an H2B-ubiquitinated nucleosome
Abstract
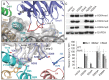
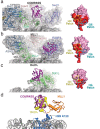
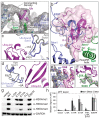
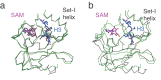
Methylation of histone H3K4 is a hallmark of actively transcribed genes that depends on mono-ubiquitination of histone H2B (H2B-Ub). H3K4 methylation in yeast is catalyzed by Set1, the methyltransferase subunit of COMPASS. We report here the cryo-EM structure of a six-protein core COMPASS subcomplex, which can methylate H3K4 and be stimulated by H2B-Ub, bound to a ubiquitinated nucleosome. Our structure shows that COMPASS spans the face of the nucleosome, recognizing ubiquitin on one face of the nucleosome and methylating H3 on the opposing face. As compared to the structure of the isolated core complex, Set1 undergoes multiple structural rearrangements to cement interactions with the nucleosome and with ubiquitin. The critical Set1 RxxxRR motif adopts a helix that mediates bridging contacts between the nucleosome, ubiquitin and COMPASS. The structure provides a framework for understanding mechanisms of trans-histone cross-talk and the dynamic role of H2B ubiquitination in stimulating histone methylation.
Keywords: S. cerevisiae; chromatin; chromosomes; gene expression; histone methylation; molecular biophysics; structural biology; transcription; ubiquitin.
© 2020, Worden et al.
Conflict of interest statement
EW, XZ No competing interests declared, CW Senior editor, eLife
Figures


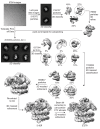
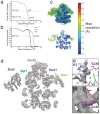
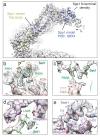
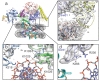


Comment in
-
Navigating the structure of COMPASS.Elife. 2020 Feb 24;9:e54767. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54767. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32091392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung L-W, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH. PHENIX : a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallographica Section D Biological Crystallography. 2010;66:213–221. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909052925. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

