Color image segmentation using adaptive hierarchical-histogram thresholding
- PMID: 31923214
- PMCID: PMC6953780
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226345
Color image segmentation using adaptive hierarchical-histogram thresholding
Abstract
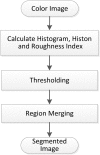
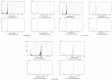
Histogram-based thresholding is one of the widely applied techniques for conducting color image segmentation. The key to such techniques is the selection of a set of thresholds that can discriminate objects and background pixels. Many thresholding techniques have been proposed that use the shape information of histograms and identify the optimum thresholds at valleys. In this work, we introduce the novel concept of a hierarchical-histogram, which corresponds to a multigranularity abstraction of the color image. Based on this, we present a new histogram thresholding-Adaptive Hierarchical-Histogram Thresholding (AHHT) algorithm, which can adaptively identify the thresholds from valleys. The experimental results have demonstrated that the AHHT algorithm can obtain better segmentation results compared with the histon-based and the roughness-index-based techniques with drastically reduced time complexity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures







References
-
- Pare S, Bhandari AK., Kumar A, Singh GK, An optimal color image multilevel thresholding technique using grey-level co-occurrence matrix, Expert Systems With Applications. 2017;87:335–362. 10.1016/j.eswa.2017.06.021 - DOI
-
- Yue XD., Miao DQ, Zhang N, Cao LB, Wu Q. Multiscale roughness measure for color image segmentation. Information Sciences. 2012; 216(24): 93–112. 10.1016/j.ins.2012.05.025. - DOI
-
- Aghbari ZA, Al-Haj R. Hill-manipulation: An effective algorithm for color image segmentation, Image & Vision Computing. 2006; 24(8): 894–903. 10.1016/j.imavis.2006.02.013 - DOI
-
- Sahoo PK., Wilkins C, Yeager J. Threshold selection using Renyi′s entropy. Pattern Recognition. 1997; 30: 71–84. 10.1016/S0031-3203(96)00065-9 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

