Influence of high affinity haemoglobin on the response to normoxic and hypoxic exercise
- PMID: 31923331
- PMCID: PMC7325343
- DOI: 10.1113/JP279161
Influence of high affinity haemoglobin on the response to normoxic and hypoxic exercise
Abstract
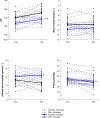
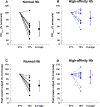
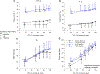
Key points: Theoretical models suggest there is no benefit of high affinity haemoglobin to preserve maximal oxygen uptake in acute hypoxia but the comparative biology literature has many examples of species that are evolutionarily adapted to hypoxia and have high affinity haemoglobin. We studied humans with high affinity haemoglobin and compensatory polycythaemia. These subjects performed maximal exercise tests in normoxia and hypoxia to determine how their altered haemoglobin affinity impacts hypoxic exercise tolerance. The high affinity haemoglobin participants demonstrated an attenuated decline in maximal aerobic capacity in acute hypoxia. Those with high affinity haemoglobin had no worsening of pulmonary gas exchange during hypoxic exercise but had greater lactate and lower pH than controls for all exercise bouts. High affinity haemoglobin and compensatory polycythaemia mitigated the decline in exercise performance in acute hypoxia through a higher arterial oxygen content and an unchanged pulmonary gas exchange.
Abstract: The longstanding dogma is that humans exhibit an acute reduction in haemoglobin (Hb) binding affinity for oxygen that facilitates adaptation to moderate hypoxia. However, many animals have adapted to high altitude through enhanced Hb binding affinity for oxygen. The objective of the study was to determine whether high affinity haemoglobin (HAH) affects maximal and submaximal exercise capacity. To accomplish this, we recruited individuals (n = 11, n = 8 females) with HAH (P50 = 16 ± 1 mmHg), had them perform normoxic and acute hypoxic (15% inspired oxygen) maximal exercise tests, and then compared their results to matched controls (P50 = 26 ± 1, n = 14, n = 8 females). Cardiorespiratory and arterial blood gases were collected throughout both exercise tests. Despite no difference in end-exercise arterial oxygen tension in hypoxia (59 ± 6 vs. 59 ± 9 mmHg for controls and HAH, respectively), the HAH subjects' oxyhaemoglobin saturation ( ) was ∼7% higher. Those with HAH had an attenuated decline in maximal oxygen uptake ( ) (4 ± 5% vs. 12 ± %, p < 0.001) in hypoxia and the change in between trials was related to the change in (r = -0.75, p < 0.0001). Compared to normoxia, the controls' alveolar-to-arterial oxygen gradient significantly increased during hypoxic exercise, whereas pulmonary gas exchange in HAH subjects was unchanged between the two exercise trials. However, arterial lactate was significantly higher and arterial pH significantly lower in the HAH subjects for both exercise trials. We conclude that HAH attenuates the decline in maximal aerobic capacity and preserves pulmonary gas exchange during acute hypoxic exercise. Our data support the comparative biology literature indicating that HAH is a positive adaptation to acute hypoxia.
Keywords: maximal oxygen uptake; oxygen delivery; pulmonary gas exchange; submaximal exercise.
© 2020 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2020 The Physiological Society.
Figures

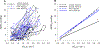



Comment in
-
With haemoglobin as with politics - should we shift right or left?J Physiol. 2020 Apr;598(8):1419-1420. doi: 10.1113/JP279555. Epub 2020 Mar 13. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32052863 No abstract available.
-
Reply from P. Dominelli, C. Wiggins, S. E. Baker, J. R. A. Shepherd, S. Roberts, T. K. Roy, T. Curry, J. Hoyer, J. L. Oliveira and M. J. Joyner.J Physiol. 2020 Aug;598(16):3533-3534. doi: 10.1113/JP280124. Epub 2020 Jun 8. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32449520 No abstract available.
-
Role of haemoglobin oxygen affinity for oxygen uptake during exercise.J Physiol. 2020 Aug;598(16):3531-3532. doi: 10.1113/JP280054. Epub 2020 Jun 24. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32449526 No abstract available.
References
-
- Arthur PG, Hogan MC, Bebout DE, Wagner PD & Hochachka PW (1992). Modeling the effects of hypoxia on ATP turnover in exercising muscle. J Appl Physiol 73, 737–742. - PubMed
-
- Aste-Salazar H & Hurtado A (1944). The affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen at sea level and at high altitudes. Am J Physiol 142, 733–743.
-
- Bencowitz HZ, Wagner PD & West JB (1982). Effect of change in P50 on exercise tolerance at high altitude: a theoretical study. J Appl Physiol 53, 1487–1495. - PubMed
-
- Berglund S (1972a). The oxygen dissociation curve of whole blood contraining haemoglobin Malmo. Scand J Haemat 9, 377–386. - PubMed
-
- Berglund S (1972b). Erythrocytosis associated with haemoglobin Malmo, accompanied by pulmonary changes, occuring in the same family. Scand J Haemat 9, 355–369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

