Mitophagy and DNA damage signaling in human aging
- PMID: 31923475
- PMCID: PMC7047626
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mad.2020.111207
Mitophagy and DNA damage signaling in human aging
Abstract
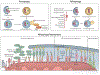
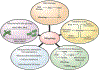
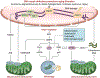
Aging is associated with multiple human pathologies. In the past few years mitochondrial homeostasis has been well correlated with age-related disorders and longevity. Mitochondrial homeostasis involves generation, biogenesis and removal of dysfunctional mitochondria via mitophagy. Mitophagy is regulated by various mitochondrial and extra-mitochondrial factors including morphology, oxidative stress and DNA damage. For decades, DNA damage and inefficient DNA repair have been considered as major determinants for age-related disorders. Although defects in DNA damage recognition and repair and mitophagy are well documented to be major factors in age-associated diseases, interactivity between these is poorly understood. Mitophagy efficiency decreases with age leading to accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria enhancing the severity of age-related disorders including neurodegenerative diseases, inflammatory diseases, cancer, diabetes and many more. Therefore, mitophagy is being targeted for intervention in age-associated disorders. NAD+ supplementation has emerged as one intervention to target both defective DNA repair and mitophagy. In this review, we discuss the molecular signaling pathways involved in regulation of DNA damage and repair and of mitophagy, and we highlight the opportunities for clinical interventions targeting these processes to improve the quality of life during aging.
Keywords: Aging; DNA damage; DNA repair; Mitochondria; Mitophagy.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


References
-
- Cohen AA, Aging across the tree of life: The importance of a comparative perspective for the use of animal models in aging. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2018. 1864(9 Pt A): p. 26802689. - PubMed
-
- Gensler HL and Bernstein H, DNA damage as the primary cause of aging. Q Rev Biol, 1981. 56(3): p. 279–303. - PubMed
-
- Stewart JB and Chinnery PF, The dynamics of mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy: implications for human health and disease. Nat Rev Genet, 2015. 16(9): p. 530–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

