Layer-by-layer pH-sensitive nanoparticles for drug delivery and controlled release with improved therapeutic efficacy in vivo
- PMID: 31924103
- PMCID: PMC7008239
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2019.1709922
Layer-by-layer pH-sensitive nanoparticles for drug delivery and controlled release with improved therapeutic efficacy in vivo
Abstract
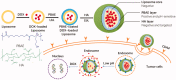
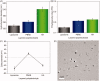
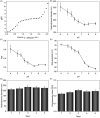
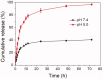
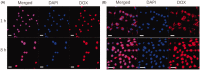
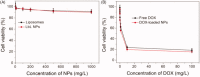
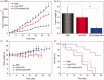
In this work, a pH-sensitive liposome-polymer nanoparticle (NP) composed of lipid, hyaluronic acid (HA) and poly(β-amino ester) (PBAE) was prepared using layer-by-layer (LbL) method for doxorubicin (DOX) targeted delivery and controlled release to enhance the cancer treatment efficacy. The NP with pH-sensitivity and targeting effect was successfully prepared by validation of charge reversal and increase of hydrodynamic diameter after each deposition of functional layer. We further showed the DOX-loaded NP had higher drug loading capacity, suitable particle size, spherical morphology, good uniformity, and high serum stability for drug delivery. We confirmed that the drug release profile was triggered by low pH with sustained release manner in vitro. Confocal microscopy research demonstrated that the NP was able to effectively target and deliver DOX into human non-small cell lung carcinoma (A549) cells in comparison to free DOX. Moreover, the blank NP showed negligible cytotoxicity, and the DOX-loaded NP could efficiently induce the apoptosis of A549 cells as well as free DOX. Notably, in vivo experiment results showed that the DOX-loaded NPs effectively inhibited the growth of tumor, enhanced the survival of tumor-bearing mice and improved the therapeutic efficacy with reduced side-effect comparing with free drug. Therefore, the NP could be a potential intelligent anticancer drug delivery carrier for cancer chemotherapy, and the LbL method might be a useful strategy to prepare multi-functional platform for drug delivery.
Keywords: Drug delivery; HA-targeting; cancer therapy; controlled release; layer-by-layer; nanoparticle; pH-sensitivity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fabrication Of Dual pH/redox-Responsive Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles For Anticancer Drug Delivery And Controlled Release.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Oct 3;14:8001-8011. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S226798. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31632014 Free PMC article.
-
Layer-by-layer coated hybrid nanoparticles with pH-sensitivity for drug delivery to treat acute lung infection.Drug Deliv. 2021 Dec;28(1):2460-2468. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.2000676. Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 34766544 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Toxicity of Doxorubicin Encapsulated into pH-Responsive Poly(β-Amino Ester)-Functionalized MCM-41 Silica Nanoparticles.Curr Drug Deliv. 2020;17(9):799-805. doi: 10.2174/1567201817999200728123915. Curr Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 32723272
-
Expert opinion: Responsive polymer nanoparticles in cancer therapy.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2012 Feb;80(2):241-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2011.08.004. Epub 2011 Aug 25. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2012. PMID: 21888972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dendrimer as a promising nanocarrier for the delivery of doxorubicin as an anticancer therapeutics.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2021 Oct;32(14):1882-1909. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2021.1938859. Epub 2021 Jul 20. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2021. PMID: 34078252 Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-Smart and Scalable Bioligands-Free Nanomedical Platform for Intratumorally Targeted Tambjamine Delivery, a Difficult to Administrate Highly Cytotoxic Drug.Biomedicines. 2021 May 4;9(5):508. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9050508. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34064518 Free PMC article.
-
Charge reversal nano-systems for tumor therapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Jan 10;20(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01221-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35012546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing engineering design strategies for targeted cancer nanomedicine.Nat Rev Cancer. 2025 Aug 1. doi: 10.1038/s41568-025-00847-2. Online ahead of print. Nat Rev Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40751005 Review.
-
Polymer-Modified Liposomes for Drug Delivery: From Fundamentals to Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Apr 2;14(4):778. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14040778. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35456613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overcoming challenges in the design of drug delivery systems targeting the central nervous system.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025 Jan;20(1):5-8. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2024.2421157. Epub 2024 Nov 20. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025. PMID: 39564781 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ariga K, Yamauchi Y, Rydzek G, et al. (2014). Layer-by-layer nanoarchitectonics: invention, innovation, and evolution. Chem Lett 43:36–68.
-
- Borges J, Mano JF. (2014). Molecular interactions driving the layer-by-layer assembly of multilayers. Chem Rev 114:8883–942. - PubMed
-
- Chen D, Yu H, Sun K, et al. (2014). Dual thermoresponsive and pH-responsive self-assembled micellar nanogel for anticancer drug delivery. Drug Deliv 21:258–64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
