The epidemiology of headaches among patients with epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 31924166
- PMCID: PMC6954535
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-020-1074-0
The epidemiology of headaches among patients with epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head or neck that causes disability in most people with medical and neurological disorders. It frequently co-occurs with most chronic diseases such as epilepsy and significantly impacts the quality of life. However, epidemiologic data from different studies showed different rates of prevalence. Therefore, we conducted this review to summarize the available epidemiologic evidence on the topic and formulate recommendations for future research and clinical practice.
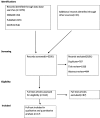
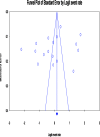
Methods: We followed the preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis (PRISMA) guidelines. We systematically searched the literature using popular databases such as PubMed, EMBASE, Psych-INFO, and SCOPUS. We further scanned the reference lists of the eligible studies to supplement our electronic search. The Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software version 3.0 (CMA 3.0) was used to conduct a meta-analysis. Subgroup and sensitivity analysis were performed and Cochran's Q- and the I2- test were used to assess the source of heterogeneity. The funnel plot and Egger's regression tests were used to assess potential publication bias.
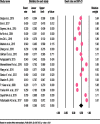
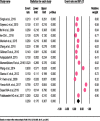
Results: A total of 17 studies conducted both in developed and developing countries including 5564 study participants were combined in this meta-analysis. The pooled estimated prevalence of headache among patients with epilepsy was 48.4%. The pooled estimated prevalence of Inter-Ictal headache (IIH) (42.2%) and Postictal headache (PIH) (43.1%) were higher when compared to tension-type headache (TTH) (26.2%), migraine with aura (26.0%) and migraine without aura (10.4%). The pooled prevalence of headache was 50.6% and 49.5% for developed and developing countries respectively. The pooled prevalence of headache among patients with epilepsy was considerably higher among females (63.0%) when compared to males (33.3%). Moreover, the pooled estimated prevalence of headache among patients with epilepsy was ranging from 46.0% to 52.2% in a leave-one-out sensitivity analysis.
Conclusion: The pooled estimated prevalence of headache among patients with epilepsy was considerably high (48.4%). Screening and appropriate management of headaches among patients with epilepsy are warranted.
Keywords: Epilepsy; Headaches; Meta-analysis; Prevalence; Seizure; Systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The epidemiology of primary headaches in patients with multiple sclerosis.Brain Behav. 2021 Jan;11(1):e01830. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1830. Epub 2020 Dec 8. Brain Behav. 2021. PMID: 33295123 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence of alcohol use disorders among people living with HIV/AIDS: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2019 Nov 14;14(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s13011-019-0240-3. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2019. PMID: 31727086 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence of premenstrual dysphoric disorder among adolescents in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ir J Med Sci. 2021 Feb;190(1):419-427. doi: 10.1007/s11845-020-02275-7. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Ir J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 32506277
-
The prevalence of depression among patients with tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2020 May 7;19:30. doi: 10.1186/s12991-020-00281-8. eCollection 2020. Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32419837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiology of depression in people living with HIV in east Africa.BMC Psychiatry. 2018 Aug 15;18(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s12888-018-1835-3. BMC Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30111300 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Primary Headache Is Related to Reduced Health-Related Quality of Life in Children with Epilepsy.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Feb 7;12(4):426. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12040426. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38391802 Free PMC article.
-
Migraine - a borderland disease to epilepsy: near it but not of it.J Headache Pain. 2024 Jan 26;25(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01719-0. J Headache Pain. 2024. PMID: 38273253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Headache in people with epilepsy.Nat Rev Neurol. 2021 Sep;17(9):529-544. doi: 10.1038/s41582-021-00516-6. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Nat Rev Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34312533 Review.
-
Clinical characteristics of headache related to epilepsy: experience from a tertiary epilepsy center.BMC Neurol. 2025 May 26;25(1):223. doi: 10.1186/s12883-025-04217-1. BMC Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40420007 Free PMC article.
-
A complex systems view on the current hypotheses of epilepsy pharmacoresistance.Epilepsia Open. 2022 Aug;7 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S8-S22. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12588. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Epilepsia Open. 2022. PMID: 35253410 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thakur KT, Albanese E, Giannakopoulos P, Jette N, Linde M, Prince MJ, et al. Neurological Disorders. 2016. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organazation . keys facts on epilepsy. 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

