Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for the diagnosis of HIV-associated tuberculous meningitis: a prospective validation study
- PMID: 31924549
- PMCID: PMC7045085
- DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30550-X
Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for the diagnosis of HIV-associated tuberculous meningitis: a prospective validation study
Abstract
Introduction: Tuberculous meningitis accounts for 1-5% of tuberculosis cases. Diagnostic delay contributes to poor outcomes. We evaluated the performance of the new Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra (Xpert Ultra) for tuberculous meningitis diagnosis.
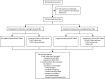
Methods: In this prospective validation study, we tested the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of adults presenting with suspected meningitis (ie, headache or altered mental status with clinical signs of meningism) to the Mulago National Referral Hospital and Mbarara Regional Referral Hospital in Uganda. We centrifuged the CSF, resuspended the cell pellet in 2 mL CSF, and tested 0·5 mL aliquots with Xpert Ultra, Xpert MTB/RIF (Xpert), and mycobacterial growth indicator tube (MGIT) culture. We quantified diagnostic performance against the uniform case definition of probable or definite tuberculous meningitis and a composite microbiological reference standard.
Findings: From Nov 25, 2016, to Jan 24, 2019, we screened 466 adults with suspected meningitis and tested 204 for tuberculous meningitis. Uniform clinical case definition classified 51 participants as having probable or definite tuberculous meningitis. Against this uniform case definition, Xpert Ultra had 76·5% sensitivity (95% CI 62·5-87·2; 39 of 51 patients) and a negative predictive value of 92·7% (87·6-96·2; 153 of 165), compared with 55·6% sensitivity (44·0-70·4; 25 of 45; p=0·0010) and a negative predictive value of 85·8% (78·9-91·1; 121 of 141) for Xpert and 61·4% sensitivity (45·5-75·6; 27 of 44; p=0·020) and negative predictive value of 85·2% (77·4-91·1; 98 of 115) for MGIT culture. Against the composite microbiological reference standard, Xpert Ultra had sensitivity of 92·9% (80·5-98·5; 39 of 42), higher than Xpert at 65·8% (48·6-80·4; 25 of 38; p=0·0063) and MGIT culture at 72·2% (55·9-86·2; 27 of 37; p=0·092). Xpert Ultra detected nine tuberculous meningitis cases missed by Xpert and MGIT culture.
Interpretation: Xpert Ultra detected tuberculous meningitis with higher sensitivity than Xpert and MGIT culture in this HIV-positive population. However, with a negative predictive value of 93%, Xpert Ultra cannot be used as a rule-out test. Clinical judgment and novel highly sensitive point-of-care tests are still required.
Funding: Wellcome Trust, National Institute of Health, National Institute of Neurologic Diseases and Stroke, Fogarty International Center, and National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- WHO . Global tuberculosis report 2019. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2019.
-
- Heemskerk AD, Bang ND, Thwaites GE. Therapy for tuberculous meningitis. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:2188–2189. - PubMed
-
- Sheu JJ, Yuan RY, Yang CC. Predictors for outcome and treatment delay in patients with tuberculous meningitis. Am J Med Sci. 2009;338:134–139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

