Trametinib Activity in Patients with Solid Tumors and Lymphomas Harboring BRAF Non-V600 Mutations or Fusions: Results from NCI-MATCH (EAY131)
- PMID: 31924734
- PMCID: PMC7165046
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-3443
Trametinib Activity in Patients with Solid Tumors and Lymphomas Harboring BRAF Non-V600 Mutations or Fusions: Results from NCI-MATCH (EAY131)
Abstract
Purpose: Substantial preclinical evidence and case reports suggest that MEK inhibition is an active approach in tumors with BRAF mutations outside the V600 locus, and in BRAF fusions. Thus, Subprotocol R of the NCI-MATCH study tested the MEK inhibitor trametinib in this population.
Patients and methods: The NCI-MATCH study performed genomic profiling on tumor samples from patients with solid tumors and lymphomas progressing on standard therapies or with no standard treatments. Patients with prespecified fusions and non-V600 mutations in BRAF were assigned to Subprotocol R using the NCI-MATCHBOX algorithm. The primary endpoint was objective response rate (ORR).
Results: Among 50 patients assigned, 32 were eligible and received therapy with trametinib. Of these, 1 had a BRAF fusion and 31 had BRAF mutations (13 and 19 with class 2 and 3 mutations, respectively). There were no complete responses; 1 patient (3%) had a confirmed partial response (patient with breast ductal adenocarcinoma with BRAF G469E mutation) and 10 patients had stable disease as best response (clinical benefit rate 34%). Median progression-free survival (PFS) was 1.8 months, and median overall survival was 5.7 months. Exploratory subgroup analyses showed that patients with colorectal adenocarcinoma (n = 8) had particularly poor PFS. No new toxicity signals were identified.
Conclusions: Trametinib did not show promising clinical activity in patients with tumors harboring non-V600 BRAF mutations, and the subprotocol did not meet its primary endpoint.
©2020 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

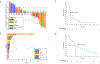

References
-
- Ascierto PA, McArthur GA, Dreno B, et al. Cobimetinib combined with vemurafenib in advanced BRAF(V600)-mutant melanoma (coBRIM): updated efficacy results from a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2016;17:1248–60. - PubMed
-
- Planchard D, Smit EF, Groen HJM, et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with previously untreated BRAF(V600E)-mutant metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: an open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 2017;18:1307–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

