Arf1-mediated lipid metabolism sustains cancer cells and its ablation induces anti-tumor immune responses in mice
- PMID: 31924786
- PMCID: PMC6954189
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-14046-9
Arf1-mediated lipid metabolism sustains cancer cells and its ablation induces anti-tumor immune responses in mice
Abstract
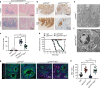
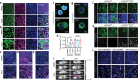
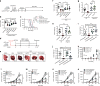
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) may be responsible for treatment resistance, tumor metastasis, and disease recurrence. Here we demonstrate that the Arf1-mediated lipid metabolism sustains cells enriched with CSCs and its ablation induces anti-tumor immune responses in mice. Notably, Arf1 ablation in cancer cells induces mitochondrial defects, endoplasmic-reticulum stress, and the release of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which recruit and activate dendritic cells (DCs) at tumor sites. The activated immune system finally elicits antitumor immune surveillance by stimulating T-cell infiltration and activation. Furthermore, TCGA data analysis shows an inverse correlation between Arf1 expression and T-cell infiltration and activation along with patient survival in various human cancers. Our results reveal that Arf1-pathway knockdown not only kills CSCs but also elicits a tumor-specific immune response that converts dying CSCs into a therapeutic vaccine, leading to durable benefits.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

