Deep learning for detecting retinal detachment and discerning macular status using ultra-widefield fundus images
- PMID: 31925315
- PMCID: PMC6949241
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-019-0730-x
Deep learning for detecting retinal detachment and discerning macular status using ultra-widefield fundus images
Abstract
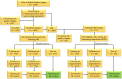
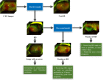
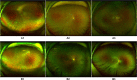
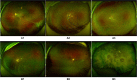
Retinal detachment can lead to severe visual loss if not treated timely. The early diagnosis of retinal detachment can improve the rate of successful reattachment and the visual results, especially before macular involvement. Manual retinal detachment screening is time-consuming and labour-intensive, which is difficult for large-scale clinical applications. In this study, we developed a cascaded deep learning system based on the ultra-widefield fundus images for automated retinal detachment detection and macula-on/off retinal detachment discerning. The performance of this system is reliable and comparable to an experienced ophthalmologist. In addition, this system can automatically provide guidance to patients regarding appropriate preoperative posturing to reduce retinal detachment progression and the urgency of retinal detachment repair. The implementation of this system on a global scale may drastically reduce the extent of vision impairment resulting from retinal detachment by providing timely identification and referral.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deep Learning for Detecting Subretinal Fluid and Discerning Macular Status by Fundus Images in Central Serous Chorioretinopathy.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Nov 5;9:651340. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.651340. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34805102 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of visual recovery with macular height in macula-off retinal detachments.Eye (Lond). 2010 Feb;24(2):323-7. doi: 10.1038/eye.2009.74. Epub 2009 Apr 24. Eye (Lond). 2010. PMID: 19390562
-
Optical coherence tomography automated layer segmentation of macula after retinal detachment repair.PLoS One. 2018 May 7;13(5):e0197058. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197058. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29734400 Free PMC article.
-
Macular hole-associated retinal detachment in Best vitelliform dystrophy: Series of two cases and literature review.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2018 May;66(5):708-711. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1046_17. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29676326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using AI for Detection, Prediction and Classification of Retinal Detachment.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2023 Jun 29;305:636-639. doi: 10.3233/SHTI230578. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2023. PMID: 37387112 Review.
Cited by
-
Automated detection of retinal exudates and drusen in ultra-widefield fundus images based on deep learning.Eye (Lond). 2022 Aug;36(8):1681-1686. doi: 10.1038/s41433-021-01715-7. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Eye (Lond). 2022. PMID: 34345030 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a computer-aided diagnostic model for corneal diseases by analyzing in vivo confocal microscopy images.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Apr 20;10:1164188. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1164188. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37153082 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning from "passive feeding" to "selective eating" of real-world data.NPJ Digit Med. 2020 Oct 30;3:143. doi: 10.1038/s41746-020-00350-y. eCollection 2020. NPJ Digit Med. 2020. PMID: 33145439 Free PMC article.
-
Semi-automated quantification of vitreal hyperreflective foci in SD-OCT and their relevance in patients with peripheral retinal breaks.BMC Ophthalmol. 2023 Jul 17;23(1):324. doi: 10.1186/s12886-023-03060-7. BMC Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37460946 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic Diagnosis of Infectious Keratitis Based on Slit Lamp Images Analysis.J Pers Med. 2023 Mar 13;13(3):519. doi: 10.3390/jpm13030519. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 36983701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hajari JN, et al. A nationwide study on the incidence of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment in denmark, with emphasis on the risk of the fellow eye. Retin. J. Ret. Vit. Dis. 2014;34:1658. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

