Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor signaling regulates inositol-requiring enzyme 1α activation to protect β-cells against terminal unfolded protein response under irremediable endoplasmic reticulum stress
- PMID: 31925927
- PMCID: PMC7378412
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.13211
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor signaling regulates inositol-requiring enzyme 1α activation to protect β-cells against terminal unfolded protein response under irremediable endoplasmic reticulum stress
Abstract
Aims/introduction: Under irremediable endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, hyperactivated inositol-requiring enzyme 1α (IRE1α) triggers the terminal unfolded protein response (T-UPR), causing crucial cell dysfunction and apoptosis. We hypothesized that nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) signaling regulates IRE1α activation to protect β-cells from the T-UPR under ER stress.
Materials and methods: The effects of nicotine on IRE1α activation and key T-UPR markers, thioredoxin-interacting protein and insulin/proinsulin, were analyzed by real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blotting in rat INS-1 and human EndoC-βH1 β-cell lines. Doxycycline-inducible IRE1α overexpression or ER stress agents were used to induce IRE1α activation. An α7 subunit-specific nAChR agonist (PNU-282987) and small interfering ribonucleic acid for α7 subunit-specific nAChR were used to modulate nAChR signaling.
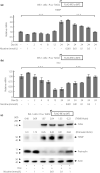
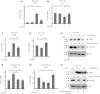
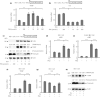
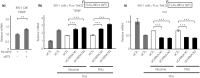
Results: Nicotine inhibits the increase in thioredoxin-interacting protein and the decrease in insulin 1/proinsulin expression levels induced by either forced IRE1α hyperactivation or ER stress agents. Nicotine attenuated X-box-binding protein-1 messenger ribonucleic acid site-specific splicing and IRE1α autophosphorylation induced by ER stress. Furthermore, PNU-282987 attenuated T-UPR induction by either forced IRE1α activation or ER stress agents. The effects of nicotine on attenuating thioredoxin-interacting protein and preserving insulin 1 expression levels were attenuated by pharmacological and genetic inhibition of α7 nAChR. Finally, nicotine suppressed apoptosis induced by either forced IRE1α activation or ER stress agents.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that nAChR signaling regulates IRE1α activation to protect β-cells from the T-UPR and apoptosis under ER stress partly through α7 nAChR. Targeting nAChR signaling to inhibit the T-UPR cascade may therefore hold therapeutic promise by thwarting β-cell death in diabetes.
Keywords: Inositol-requiring enzyme 1α; Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; Pancreatic β cell.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IRE1α induces thioredoxin-interacting protein to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome and promote programmed cell death under irremediable ER stress.Cell Metab. 2012 Aug 8;16(2):250-64. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.07.007. Cell Metab. 2012. PMID: 22883233 Free PMC article.
-
The endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor IRE1α protects cells from apoptosis induced by the coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus.J Virol. 2014 Nov;88(21):12752-64. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02138-14. Epub 2014 Aug 20. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25142592 Free PMC article.
-
ER stress and the decline and fall of pancreatic beta cells in type 1 diabetes.Ups J Med Sci. 2016 May;121(2):133-9. doi: 10.3109/03009734.2015.1135217. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Ups J Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 26899404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bax Inhibitor-1 preserves pancreatic β-cell proteostasis by limiting proinsulin misfolding and programmed cell death.Cell Death Dis. 2024 May 14;15(5):334. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06701-x. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38744890 Free PMC article.
-
IRE1α-mediated UPR activation in gastrointestinal cancers: Adaptive mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Drug Discov Today. 2025 Apr;30(4):104335. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2025.104335. Epub 2025 Mar 15. Drug Discov Today. 2025. PMID: 40097091 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic potential of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists to combat obesity, diabetes, and inflammation.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2020 Dec;21(4):431-447. doi: 10.1007/s11154-020-09584-3. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2020. PMID: 32851581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Melatonin: a Focus on the Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome.Inflammation. 2021 Aug;44(4):1207-1222. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01428-9. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 33651308 Review.
-
Living Dangerously: Protective and Harmful ER Stress Responses in Pancreatic β-Cells.Diabetes. 2021 Nov;70(11):2431-2443. doi: 10.2337/dbi20-0033. Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 34711668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YAP-Dependent BiP Induction Is Involved in Nicotine-Mediated Oral Cancer Malignancy.Cells. 2021 Aug 13;10(8):2080. doi: 10.3390/cells10082080. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440849 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Adaptive IRE1α Signaling and PLK2 in Multiple Myeloma: Possible Anti-Tumor Mechanisms of KIRA8 and Nilotinib.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 31;21(17):6314. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176314. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32878237 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ron D, Walter P. Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007; 8: 519–529. - PubMed
-
- Hetz C, Papa FR. The unfolded protein response and cell fate control. Mol Cell 2018; 69: 169–181. - PubMed
-
- Walter P, Ron D. The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 2011; 334: 1081–1086. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

