OpenSFDI: an open-source guide for constructing a spatial frequency domain imaging system
- PMID: 31925946
- PMCID: PMC7008504
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JBO.25.1.016002
OpenSFDI: an open-source guide for constructing a spatial frequency domain imaging system
Abstract
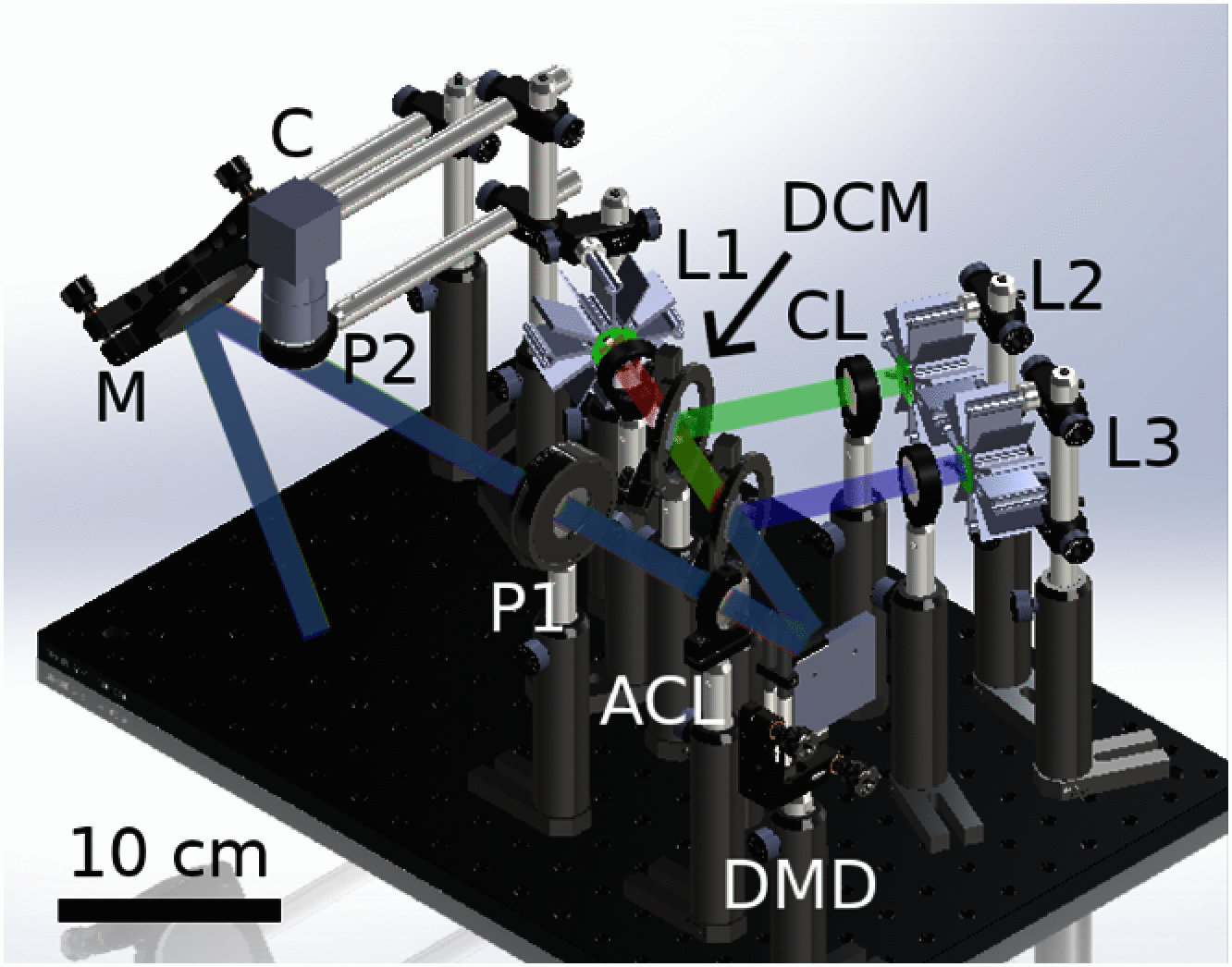
Significance: Spatial frequency domain imaging (SFDI) is a diffuse optical measurement technique that can quantify tissue optical absorption (μa) and reduced scattering (<inline-formula></inline-formula>) on a pixel-by-pixel basis. Measurements of μa at different wavelengths enable the extraction of molar concentrations of tissue chromophores over a wide field, providing a noncontact and label-free means to assess tissue viability, oxygenation, microarchitecture, and molecular content. We present here openSFDI: an open-source guide for building a low-cost, small-footprint, three-wavelength SFDI system capable of quantifying μa and <inline-formula></inline-formula> as well as oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin concentrations in biological tissue. The companion website provides a complete parts list along with detailed instructions for assembling the openSFDI system.<p> Aim: We describe the design of openSFDI and report on the accuracy and precision of optical property extractions for three different systems fabricated according to the instructions on the openSFDI website.</p> <p> Approach: Accuracy was assessed by measuring nine tissue-simulating optical phantoms with a physiologically relevant range of μa and <inline-formula></inline-formula> with the openSFDI systems and a commercial SFDI device. Precision was assessed by repeatedly measuring the same phantom over 1 h.</p> <p> Results: The openSFDI systems had an error of 0 ± 6 % in μa and -2 ± 3 % in <inline-formula></inline-formula>, compared to a commercial SFDI system. Bland-Altman analysis revealed the limits of agreement between the two systems to be ± 0.004 mm - 1 for μa and -0.06 to 0.1 mm - 1 for <inline-formula></inline-formula>. The openSFDI system had low drift with an average standard deviation of 0.0007 mm - 1 and 0.05 mm - 1 in μa and <inline-formula></inline-formula>, respectively.</p>,<p> Conclusion: The openSFDI provides a customizable hardware platform for research groups seeking to utilize SFDI for quantitative diffuse optical imaging.</p>
Keywords: diffuse optics; frequency domain; modulated imaging; open source; optical properties; spatial frequency domain imaging.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Hyperspectral imaging in the spatial frequency domain with a supercontinuum source.J Biomed Opt. 2019 Jul;24(7):1-9. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.24.7.071614. J Biomed Opt. 2019. PMID: 31271005 Free PMC article.
-
Visible spatial frequency domain imaging with a digital light microprojector.J Biomed Opt. 2013 Sep;18(9):096007. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.18.9.096007. J Biomed Opt. 2013. PMID: 24005154 Free PMC article.
-
Shortwave infrared spatial frequency domain imaging for non-invasive measurement of tissue and blood optical properties.J Biomed Opt. 2022 Jun;27(6):066003. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.27.6.066003. J Biomed Opt. 2022. PMID: 35715883 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative In Vivo Imaging of Tissue Absorption, Scattering, and Hemoglobin Concentration in Rat Cortex Using Spatially Modulated Structured Light.In: Frostig RD, editor. In Vivo Optical Imaging of Brain Function. 2nd edition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2009. Chapter 12. In: Frostig RD, editor. In Vivo Optical Imaging of Brain Function. 2nd edition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2009. Chapter 12. PMID: 26844326 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Spatial frequency domain imaging in 2019: principles, applications, and perspectives.J Biomed Opt. 2019 Jun;24(7):1-18. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.24.7.071613. J Biomed Opt. 2019. PMID: 31222987 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Perspective on the increasing role of optical wearables and remote patient monitoring in the COVID-19 era and beyond.J Biomed Opt. 2020 Oct;25(10):102703. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.25.10.102703. J Biomed Opt. 2020. PMID: 33089674 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial Frequency Domain Imaging System Calibration, Correction and Application for Pear Surface Damage Detection.Foods. 2021 Sep 11;10(9):2151. doi: 10.3390/foods10092151. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34574261 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of compressive sensing in spatial frequency domain imaging.J Biomed Opt. 2020 Nov;25(11):112904. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.25.11.112904. J Biomed Opt. 2020. PMID: 33179460 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of optical aberrations on depth-specific spatial frequency domain techniques.J Biomed Opt. 2022 Nov;27(11):116003. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.27.11.116003. J Biomed Opt. 2022. PMID: 36358008 Free PMC article.
-
Development and characterization of a combined fluorescence and spatial frequency domain imaging system for real-time dosimetry of photodynamic therapy.J Biomed Opt. 2025 Dec;30(Suppl 3):S34103. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.30.S3.S34103. Epub 2025 May 28. J Biomed Opt. 2025. PMID: 40443947 Free PMC article.

