Alteration of movement patterns in low back pain assessed by Statistical Parametric Mapping
- PMID: 31928738
- PMCID: PMC7001037
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2019.109597
Alteration of movement patterns in low back pain assessed by Statistical Parametric Mapping
Abstract
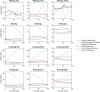
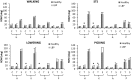
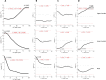
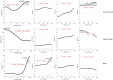
Changes in movement pattern in low back pain (LBP) groups have been analysed by reporting predefined discrete variables. However, this approach does not consider the full kinematic data waveform and its dynamic information, potentially exposing the analysis to bias. Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM) has been introduced and applied to 1 dimensional (D) kinematic variables allowing the assessment of data over time. The aims of this study were to assess differences in 3D kinematics patterns in people with and without LBP during functional tasks by using SPM and to investigate if SPM analysis was consistent with standard 3D range of motion (RoM) assessments. 3D joints kinematics of the spine and lower limbs were compared between 20 healthy controls and 20 participants with non-specific LBP during walking, sit-to-stand and lifting. SPM analysis showed significant differences in the 3Dkinematics of the lower thoracic segment, upper and lower lumbar segment and knee joint during walking and lifting mostly observed at the beginning and/or towards the end of the tasks. ROMs differed between groups in the lower thoracic segment (walking/sit-to-stand), upper and lower lumbar segments (walking/sit-to-stand/lifting), hip and knee (sit-to-stand/lifting). Based on these results, the two approaches can yield different data interpretations. SPM analysis allows the identification of differences in movement that occur over time. This adds value to LBP movement analysis as it allows an understanding of the LBP strategies adopted during motion that may not be conveyed by simple discrete parameters such as ROMs.
Keywords: 3D motion analysis; Kinematics; Range of motion; Time series analysis.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Adler R.J., Taylor J.E. Springer; NewYork: 2007. Random Fields and Geometry.
-
- Banks J., Chang W., Xu X., Chang C. Using horizontal heel displacement to identify heel strike instants in normal gait. Gait & Posture. 2015;42:101–103. - PubMed
-
- Cao J., Worsley K.J. The detection of local shape changes via the geometry of Hotelling's T2 fields. Ann. Stat. 1999;27:925–942.
-
- Christe G., Redhead L., Legrand T., Jolles B., Favre J. Multi-segment analysis of spinal kinematics during sit-to-stand in patients with chronic low back pain. J. Biomech. 2016;49:2060–2067. - PubMed
-
- Christe G., Kade F., Jolles B., Favre J. Chronic low back pain patients walk with locally altered spinal kinematics. J. Biomech. 2017;60:211–218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

