Surgery/Anesthesia disturbs mitochondrial fission/fusion dynamics in the brain of aged mice with postoperative delirium
- PMID: 31929114
- PMCID: PMC6977661
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.102659
Surgery/Anesthesia disturbs mitochondrial fission/fusion dynamics in the brain of aged mice with postoperative delirium
Abstract
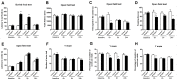
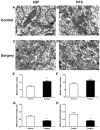
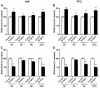
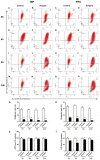
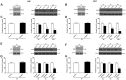
Postoperative delirium (POD) is a common complication following surgery and anesthesia (Surgery/Anesthesia). Mitochondrial dysfunction, which is demonstrated by energy deficits and excessively activated oxidative stress, has been reported to contribute to POD. The dynamic balance between mitochondrial fusion and fission processes is critical in regulating mitochondrial function. However, the impact of Surgery/Anesthesia on mitochondrial fusion/fission dynamics remains unclear. Here, we evaluate the effects of laparotomy under 1.4% isoflurane anesthesia for 2 hours on mitochondrial fission/fusion dynamics in the brain of aged mice. Mice in Surgery/Anesthesia group showed unbalanced fission/fusion dynamics, with decreased DISC1 expression and increased expression of Drp1 and Mfn2 in the mitochondrial fraction, leading to excessive mitochondrial fission and disturbed mitochondrial morphogenesis in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. In addition, surgical mice presented mitochondrial dysfunction, demonstrated by abnormally activated oxidative stress (increased ROS level, decreased SOD level) and energy deficits (decreased levels of ATP and MMP). Surgery/Anesthesia also decreased the expression of neuronal/synaptic plasticity-related proteins such as PSD-95 and BDNF. Furthermore, Surgery/Anesthesia induced delirium-like behavior in aged mice. In conclusion, Surgery/Anesthesia disturbed mitochondrial fission/fusion dynamics and then impaired mitochondrial function in the brain of aged mice; these effects may be involved in the underlying mechanism of POD.
Keywords: hippocampus; mitochondrial dynamics; mitochondrial function; postoperative delirium; prefrontal cortex.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Anesthesia and surgery induce age-dependent changes in behaviors and microbiota.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Jan 24;12(2):1965-1986. doi: 10.18632/aging.102736. Epub 2020 Jan 24. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 31974315 Free PMC article.
-
Early exposure to general anesthesia disturbs mitochondrial fission and fusion in the developing rat brain.Anesthesiology. 2013 May;118(5):1086-97. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e318289bc9b. Anesthesiology. 2013. PMID: 23411726 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated Ketamine Anesthesia during the Neonatal Period Impairs Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Long-Term Neurocognitive Function by Inhibiting Mfn2-Mediated Mitochondrial Fusion in Neural Stem Cells.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Aug;61(8):5459-5480. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-03921-2. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38200350
-
Mitochondrial fusion/fission dynamics in neurodegeneration and neuronal plasticity.Neurobiol Dis. 2016 Jun;90:3-19. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.10.011. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Neurobiol Dis. 2016. PMID: 26494254 Review.
-
Mitochondrial dynamics in type 2 diabetes: Pathophysiological implications.Redox Biol. 2017 Apr;11:637-645. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.01.013. Epub 2017 Jan 16. Redox Biol. 2017. PMID: 28131082 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Delirium in the ICU: how much do we know? A narrative review.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2405072. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2405072. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 39308447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Netrin-1 Ameliorates Postoperative Delirium-Like Behavior in Aged Mice by Suppressing Neuroinflammation and Restoring Impaired Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Jan 14;14:751570. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.751570. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35095412 Free PMC article.
-
The hotspots and publication trends in postoperative delirium: A bibliometric analysis from 2000 to 2020.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Sep 26;14:982154. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.982154. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36225889 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and stem cell factor (SCF) maintained the stemness of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (hBMSCs) during long-term expansion by preserving mitochondrial function via the PI3K/AKT, ERK1/2, and STAT3 signaling pathways.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Jul 31;11(1):329. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01830-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32736659 Free PMC article.
-
Ferrostatin-1 inhibits fibroblast fibrosis in keloid by inhibiting ferroptosis.PeerJ. 2024 Jun 14;12:e17551. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17551. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38887622 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aldecoa C, Bettelli G, Bilotta F, Sanders RD, Audisio R, Borozdina A, Cherubini A, Jones C, Kehlet H, MacLullich A, Radtke F, Riese F, Slooter AJ, et al.. European Society of Anaesthesiology evidence-based and consensus-based guideline on postoperative delirium. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2017; 34:192–214. 10.1097/EJA.0000000000000594 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

